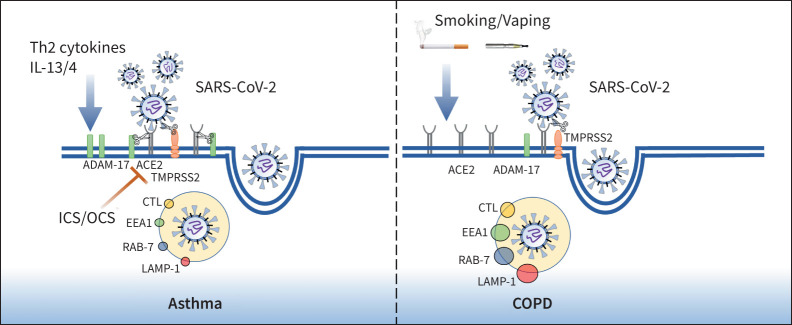
FIGURE 1.
Cellular mechanisms of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection in asthma and COPD. Smoking and vaping exposure upregulates angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) receptor expression in airway epithelium while inhaled corticosteroids (ICS) and oral corticosteroids (OCS) reduce ACE2 expression in asthma compared to COPD. Once SARS-CoV-2 binds to the ACE2 receptor via the spike protein, serine protease TMPRSS2 cleaves the viral spike protein, facilitating viral uptake and internalisation by endocytosis. The endosome- and lysosome-associated proteins EEA1, RAB-7, LAMP-1 and CTL, which facilitate viral replication within the host cell, are abundant in COPD epithelium. Th2 cytokines (IL-13) upregulate ADAM-17 expression in asthma epithelium, resulting in ACE2 shedding prior to infection.