Figure 2. Single and bi-allelic loss of Dino renders p53 progressively hypomorphic and impairs tumor suppression.
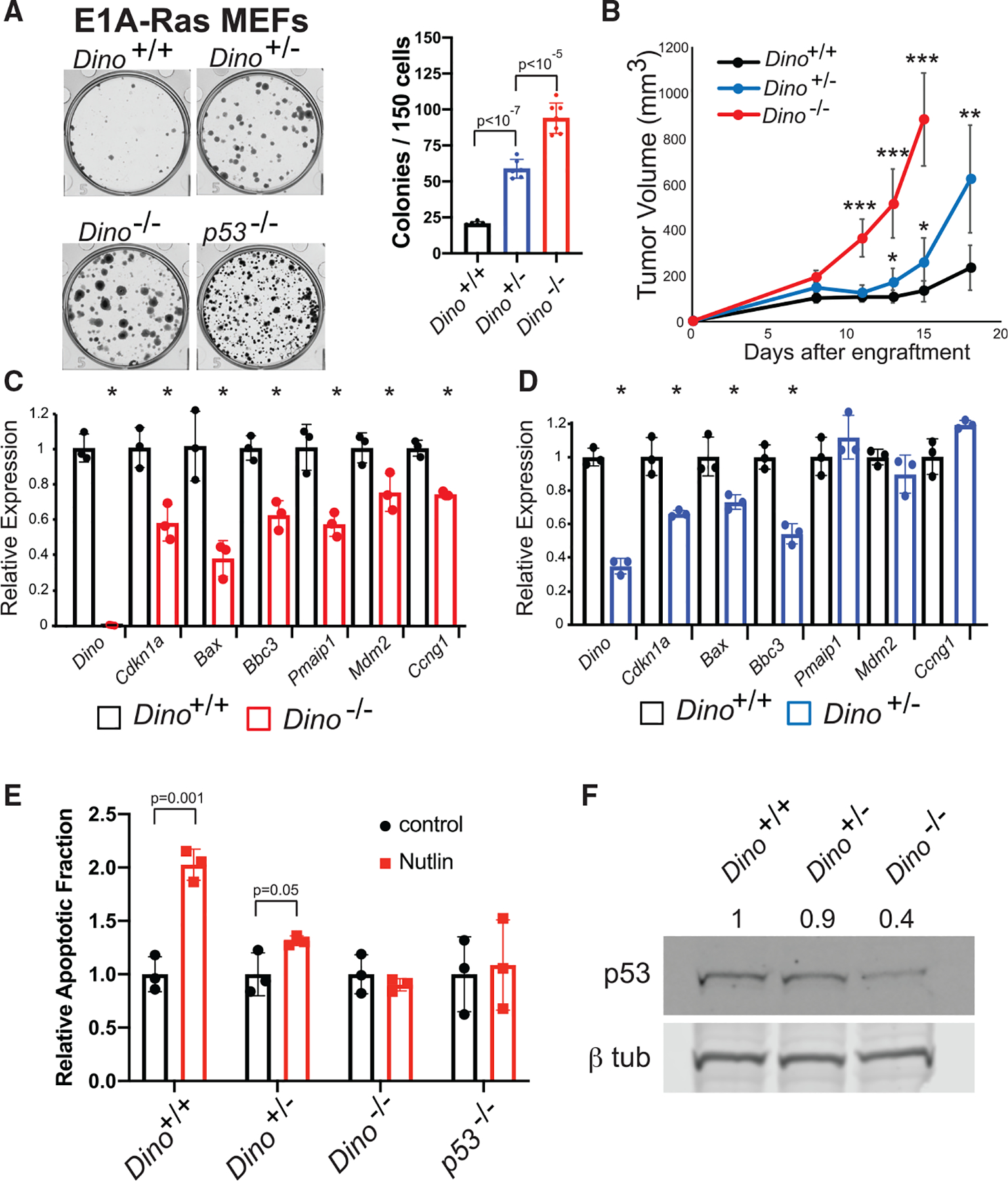
(A) In vitro clonogenic growth of Dino+/+, Dino+/−, and Dino−/− MEFs after transformation with E1A and HrasG12V retroviruses, mean ± SD, two-tailed t test.
(B) Fibrosarcoma formation in SCID mice after subcutaneous engraftment of 106 E1A-HrasG12V MEFs of indicated genotypes (mean ± SD, ***p < 10−7, **p = 0.001, *p < 0.01, two-tailed t test).
(C and D) The expression of p53-induced genes in Dino−/− E1A-HrasG12V cells (C) and Dino+/− E1A-HrasG12V cells (D) relative to Dino+/+ E1A-HrasG12V controls. (C) Mean ± SD, Dino, p = 2 × 10−5, Cdkn1a, p = 0.009, Bax, p = 0.008, Bbc3, p = 0.004, Pmaip1, p = 0.007, Mdm2, p = 0.03, Ccng1, p = 0.0007, two-tailed t test. (D) Mean ± SD, Dino, p = 10−4, Cdkn1a, p = 0.007, Bax, p = 0.02, Bbc3, p = 0.001, two-tailed t test.
(E) Apoptosis in Dino+/+, Dino+/−, Dino−/−, and p53−/−, E1A HrasG12V cells after 2.5 μM Nutlin-3a treatment, (mean ± SD, two-tailed t test).
(F) Western blot of p53 and β-tubulin in Dino+/+, Dino+/−, Dino−/− E1A HrasG12V cells with normalized p53 protein quantification.
See also Figure S3.
