Figure 5.
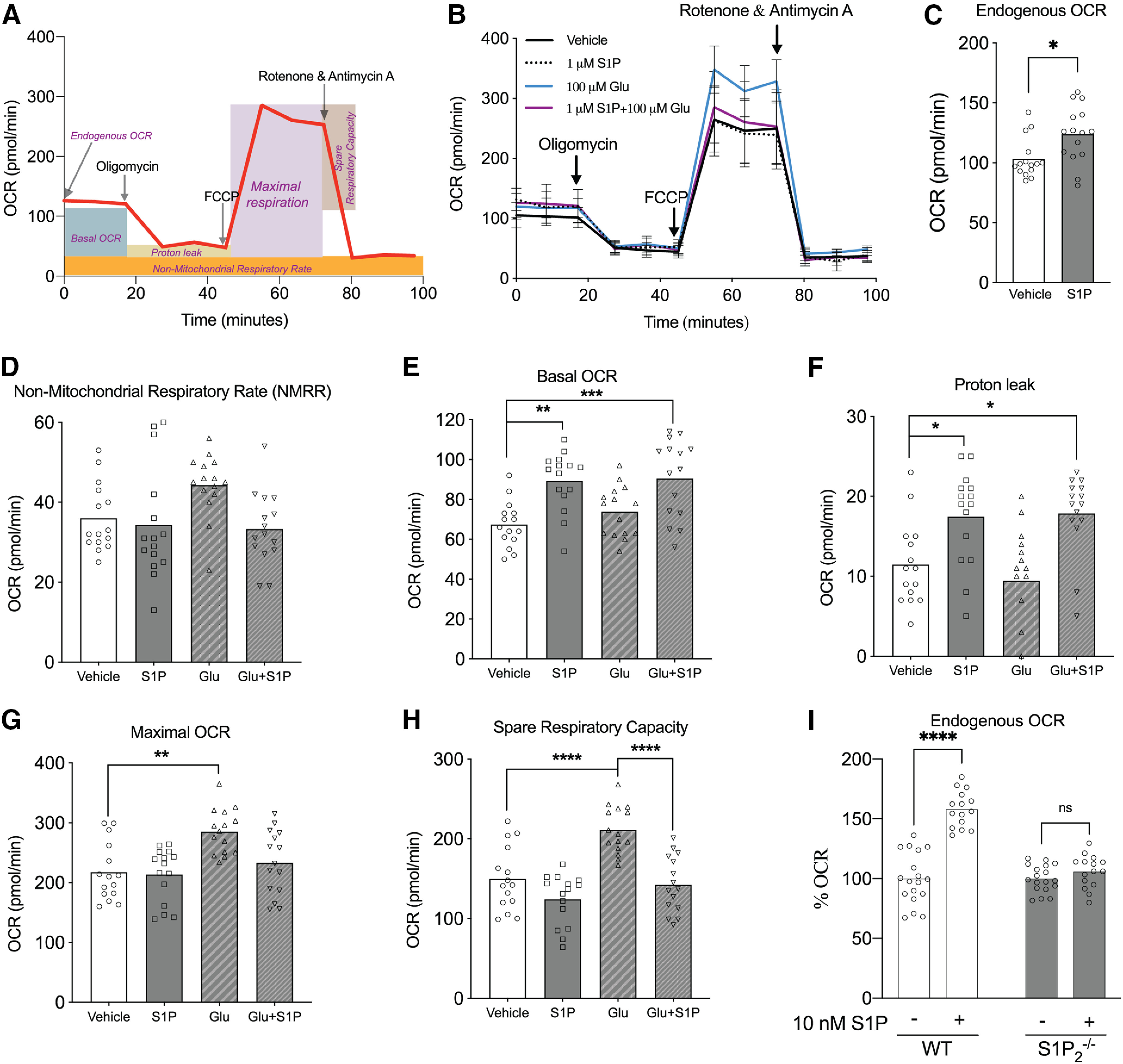
S1P increases astrocyte mitochondrial oxygen consumption rate (OCR) that is S1P2 dependent. A, Schematic of Seahorse Mito Stress analysis. B, Primary astrocytes were exposed to four conditions: vehicle, 100 μM glutamate, 1 μM S1P, or a combination of glutamate and S1P for 1 h at 37°C. After washing, Seahorse assay medium containing 1 mM pyruvate and 10 mM glucose was added and the OCR measured with an Agilent Seahorse XF24 Cell Mito Stress kit. OCR was measured three times per injection and was read in triplicate. C, S1P increased endogenous OCR when compared with vehicle *p < 0.05 unpaired t test. Non-mitochondrial respiratory rate (NMMR = OCR after rotenone/antimycin A addition; D), basal OCR (= endogenous OCR – NMRR; E), maximal OCR (= OCR after FCCP addition – NMRR; F), proton leak (= OCR after oligomycin injection – NMRR; G), and spare respiratory capacity (= maximal OCR – basal OCR; H) is represented under different conditions as indicated, n = 5 with OCR measured in triplicate at each step. Data are representative of two independent experiments with similar results. D–H, Ordinary one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.005, ***p ≤ 0.0005, ****p < 0.0001). I, Wild-type and S1P2 null primary astrocytes were incubated with Seahorse assay medium containing 1 mM pyruvate and 10 mM glucose followed by treatment with 10 nM S1P for 1 h. OCR was then measured using the Agilent Seahorse XF24 analyzer. % OCR in the presence of S1P was calculated with respect to vehicle as indicated, ****p < 0.0001, two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test. ns, not significant.
