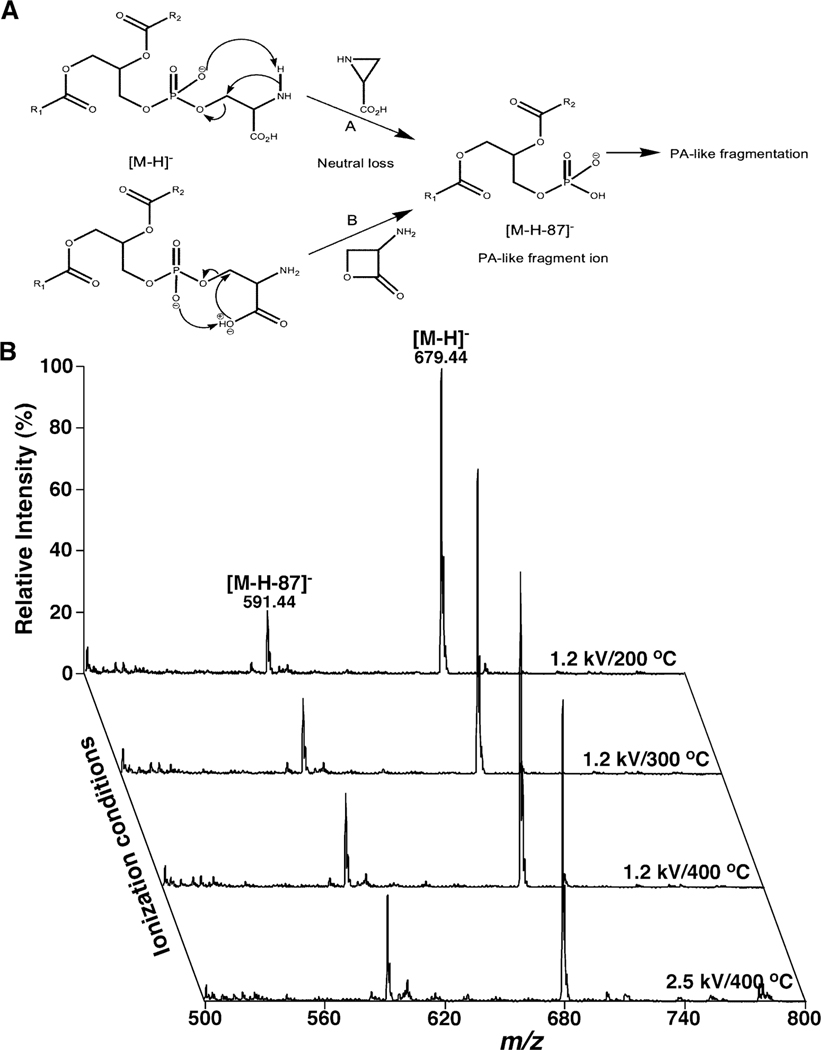
Figure 1.
Representative demonstration of PA artifacts resulted from in-source fragmentation of PS counterparts. (A) The fragmentation pathways proposed for formation of the deprotonated PA ion from PS after CID (Hsu & Turk, 2005). (B) Comparison of the ESI mass spectra of deprotonated di14:0 PS (m/z 679.4) acquired in the negative-ion mode at different conditions of temperature or spray voltage. The spectra were acquired on a QqQ mass spectrometer (Thermo Fisher TSQ Quantiva) equipped with an automated nanospray ion source (TriVersa NanoMate, Advion Bioscience Ltd.) and displayed after normalization to the base peaks. The PS species undergo in-source fragmentation to produce the PA fragment ion at m/z 591.4. The relative abundance of the PA artifact normalized to that of the PS molecular ion reflects the extent of in-source fragmentation. PA and PS denote phosphatidic acid and phosphatidylserine, respectively.