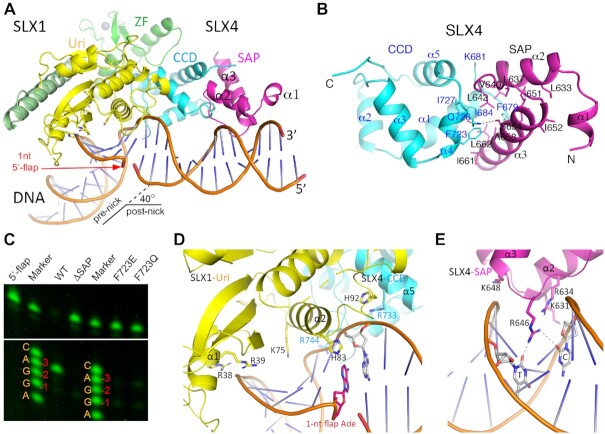
Figure 4.
Structure of SLX1–SLX4SAP+CCD bound to a 1-nt 5′-flap DNA. (A) A cartoon representation of the structure, with the SAP domain of SLX4 colored in magenta, DNA in orange, and the rest of the protein domains as in Figure 1. The location of the 1-nt flap is indicated with a red arrowhead. (B) A detailed view of packing interaction between the CCD and SAP domains of SLX4. Note that the conserved F723 of the CCD domain occupies a central position at the inter-domain interface. (C) Interference of the CCD-SAP interaction by the F723E and F723Q mutants impairs cleavage at the -3 position exhibited by the WT SLX1- SLX4SAP+CCD complex, much like with the removal of the entire SAP domain (ΔSAP), as judged by single-nucleotide resolution gel electrophoresis. The DNA marker is a mixture of synthetic DNA oligos all with a 5′-Cy3 label, carrying the XO-1 oligo sequence, as listed in Supplementary Table S1 (also see the right bottom panel of Figure 5D), but with the 3′-most nucleotide ending at –4 (C), –3 (A), –2 (G), –1 (G), +1 (A), etc., as labeled. (D) Protein-DNA interaction involving the Uri domain of SLX1 (yellow) and the CCD domain of SLX4 (cyan). The involved residues are shown as sticks. (E) The SAP domain of SLX4 (magenta) contacts DNA principally via charge interaction, and the involved residues and bases are shown.