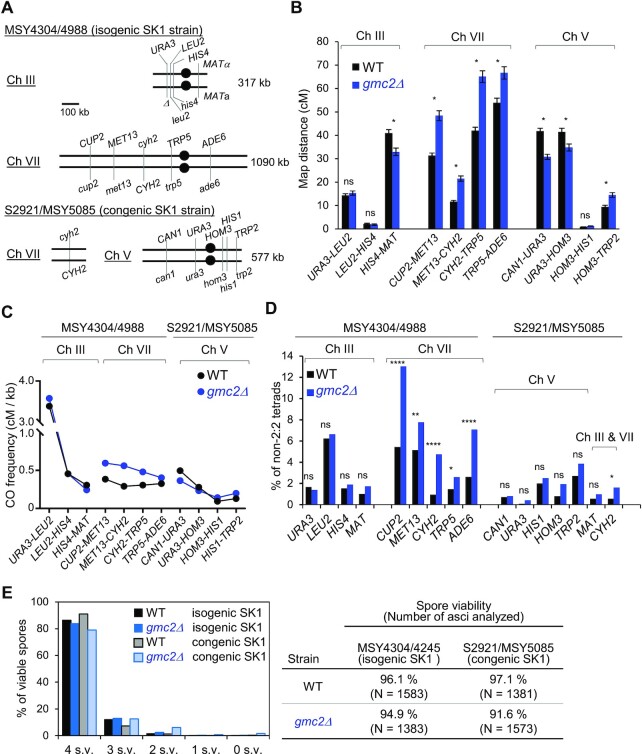
Figure 1.
The Ecm11–Gmc2 (EG) complex regulates meiotic recombination in a chromosome-dependent manner. (A) Schematic representation of the location of marker genes on chromosomes III and VII in the MSY4304/4998 diploid and chromosomes VII and V in the S2921/MSY5085 diploid. (B) Map distances within each indicated genetic interval of chromosomes III, VII, and V in the WT (black) and gmc2Δ (blue) strains determined using the Perkins equation. Error bars show standard errors (SEs). The SEs for map distances were calculated using the Stahl Lab online tool (https://elizabethhousworth.com/StahlLabOnlineTools/). The asterisks indicate significant differences between map distances in WT and gmc2Δ tetrads (see also Supplementary Table S2). ns, not significant. (C) CO frequencies (cM) per physical length (kb) of each genetic interval of chromosomes III, VII, and V in the WT and gmc2Δstrains. (D) Frequencies of non-Mendelian segregation of the indicated genetic loci in tetrads of WT and gmc2Δ strains. (E) Distribution of viable spores per tetrad (left) and spore viability in each strain (right).