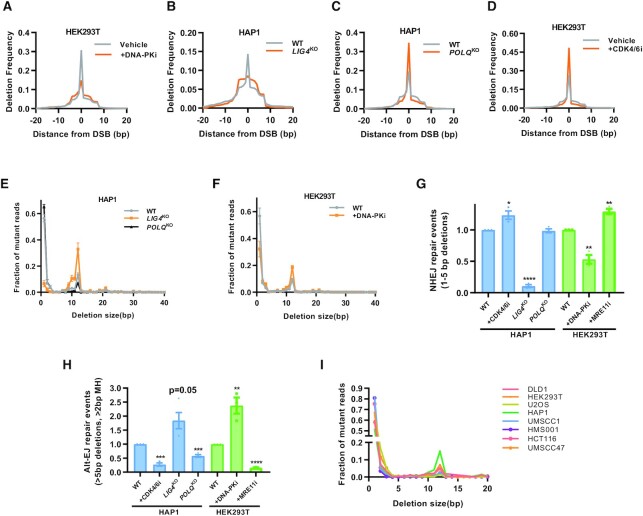
Figure 2.
Cas9 induces patterned deletions with characteristic tradeoffs between NHEJ and Alt-EJ. (A–D) Deletion size profile at the AAVS1 locus relative to position of the DSB cut site. DNA-PK inhibitor (Nu7441, 1 μM) or CDK4/6 inhibitor (Palbociclib,1 μM) in (A) and (D). Isogenic WT and LIG4KO and POLQKO cells created via CRISPR/Cas9 knockout in the HAP1 cell type background in (B) and (C). Single representative experiment shown (n = 3). (E, F) Deletion frequency by deletion length in isogenic HAP1 WT, LIG4KO and POLQKO cells in E and in HEK293T cells with or without DNA-PK inhibition (Nu7441, 1 μM) in (F). Mean ± SEM in three experiments shown. (G) NHEJ repair events, defined as deletions 1–5 bp in size and normalized to the wild type condition in HAP1 and HEK293T cells. Mean ± SEM in 3–4 experiments shown. (H) Alt-EJ repair events, defined as deletions >5 bp and utilizing >2 bp of microhomology and normalized to the wild type condition. Mean ± SEM in 3–4 experiments shown. (I) Panel of eight cell lines and distribution of deletions by size. Asterisks signify t-tests as follows: * P< 0.05, **P< 0.01, ***P< 0.001, ****P< 0.0001.