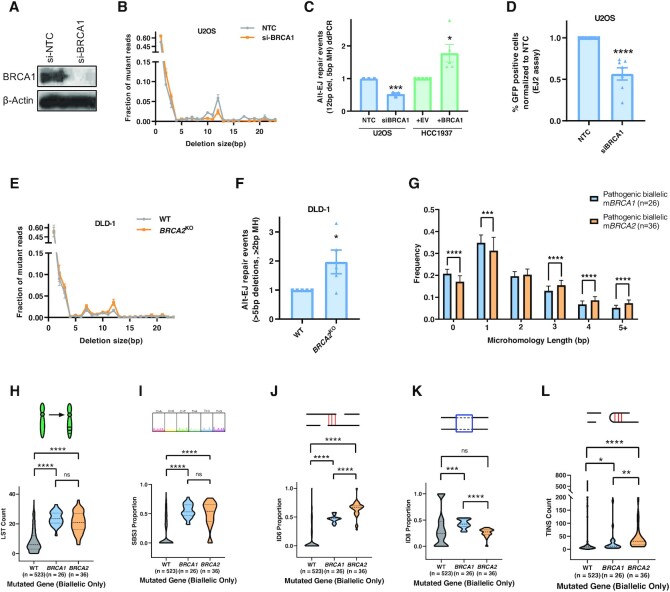
Figure 6.
BRCA1 loss suppresses Alt-EJ. (A) Confirmation of BRCA1 knockdown in U2OS cells using si-BRCA1. Beta-actin is used as a loading control. (B) Deletion frequency by deletion length in U2OS cells treated with NTC and si-BRCA1 after Cas9 breaks at the AAVS1 locus. (C) Alt-EJ repair events in U2OS cells after BRCA1 knockdown as measured using the Alt-EJ ddPCR readout (blue). Alt-EJ by ddPCR in BRCA1-deficient HCC1937 cells complemented with either BRCA1 or empty vector (green). (D) Alt-EJ repair in U2OS cells after BRCA1 knockdown measured using the EJ-2 system. (E, F) Deletion frequency by deletion length and Alt-EJ repair events in isogenic DLD-1 WT and BRCA2KO cell lines using NGS. (G) Frequency of deletions with varying microhomology lengths identified by the Pan-Cancer Analysis of Whole-Genomes (PCAWG) consortium in BRCA1 and BRCA2 biallelic mutated prostate, pancreatic, breast, and ovarian cancer patients. (H–L) Large-scale state transitions (LST) [H], single base substitution pattern 3 (SBS3) [I], ID6 [J], ID8 [K] and templated insertions (TINS) [L] signatures in WT, BRCA1 biallelic mutated, and BRCA2 biallelic mutated prostate, pancreatic, breast, and ovarian cancer patients. All P-values obtained through unpaired, two-tailed Mann–Whitney tests in GraphPad. Asterisks signify t-tests as follows: * P< 0.05, **P< 0.01, ***P< 0.001, ****P< 0.0001.