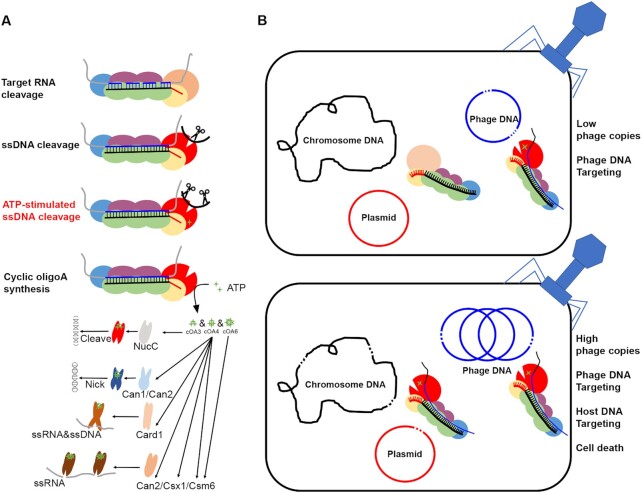
Figure 7.
Mechanisms of immunization provided by Type III-A CRISPR–Cas systems. (A) The immunization mechanism of type III CRISPR–Cas systems. Four enzymatic activities were found, including (i) crRNA-guided backbone RNase, (ii) target RNA-activated ssDNase, (iii) target RNA-dependent and ATP-stimulated ssDNase, (iv) target RNA-activated synthetase, producing a cyclic oligoadenylate (cOAn) second messengers that activate CRISPR–Cas associated proteins such as NucC, Can1, Can2, Card1, Csx1 and Csm6. (B) A model for immunization by the LdCsm system. At a low level of target RNAs, active LdCsm effectors are formed in a close proximity to phage DNA. At a high level of target RNAs, active LdCsm effectors are formed in close proximity to chromosomal DNA. In the latter scenario, LdCsm effectors will mediate DNA cleavage to any nearby transcriptional bubbles, many of which are the chromosomal ones. Thus, LdCsm can facilitate cell death to infected cells.