Figure 12.
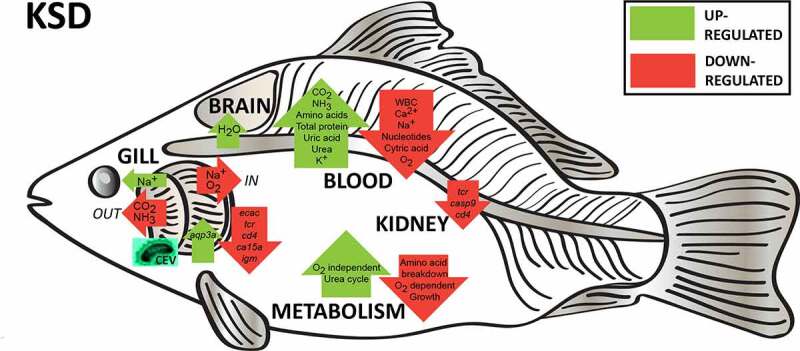
A summary of current results showing that koi sleepy disease is triggered by the gill pathology caused by the infection with carp edema virus. This impairs the respiratory, excretory and osmoregulatory function of gills, leading to a decrease in blood oxygenation and increase in CO2 content. This is compensated by a shift from oxygen-dependent to oxygen-independent metabolism and restricted growth of fish, which is reflected in a decrease in citric acid and nucleotide content in blood. Increased loss of ions via damaged gills causes hyponatremia and hypocalcemia. Further cell damage initiates hyperpotassaemia. Impairment of ammonia secretion induces hyperammonemia. This leads to a stop in ammino acid breakdown and increased urea cycle, causing the increase in amino acids, urea and uric acid content in blood. Hyponatremia and hyperammonemia could be associated with the influx of water to the brain and immunosuppression shown as downregulation of cd4, casp9, tcr a2 expression in gills and kidney and igm in gills
