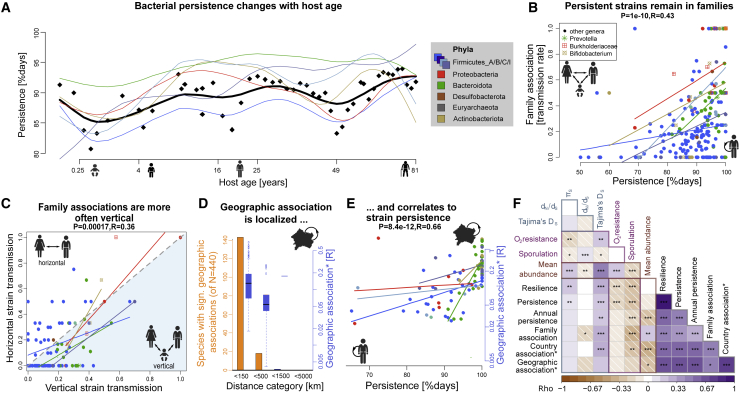
Figure 2.
Gut bacterial persistence extends beyond the individual host association
(A) Strain persistence consistently increased with host age. The black line is the average, colored lines the six most abundant phyla. Average persistence was highest in Bacteroidota strains, especially in infants (green line). Dots are the average values in each age window, lines are smoothed splines of data points. Each individual host is represented as their median age. See Figure S2 for delineation of antibiotic exposed hosts. The same taxa colors are used in all panels unless otherwise noted.
(B) Species that are persistent in an individual have a higher probability of being transmitted within a family.
(C) The frequency of vertical transmission in families (parent-child, n = 203 pairs) was often higher than horizontal transmission (parent-parent, n = 13 pairs). Species with <2 potential transmissions (total, vertically and horizontally, and arbitrary threshold) were excluded.
(D) For most of the 440 microbial species, geographic associations were only significant at a local scale (<150 km, 142/440 species, orange bars). The strength of geographic association decreased on average at higher distances (measured as the correlation coefficient between genetic and geographic distance, blue boxplots). Boxplot centers represent the median; the edges represent first and third quartiles.
(E) Persistence and geographic association (across all distance classes, only significant values included) were highly correlated; Bacteroidota (green) and Actinobacteriota (ochre) were notable for their steep correlations. Only species with significant geographic associations were included.
(F) Correlogram of the most important population genetic parameters (synonymous nucleotide diversity [πS], excess of rare alleles [Tajima’s Ds at synonymous sites], non-synonymous to synonymous substitutions [dN/dS]), and how they correlate with different forms of bacterial persistence, family, and phylogeography as well as species’ mean abundance. Stars denote multiple testing corrected Spearman correlation tests: ∗q < 0.05, ∗∗q < 0.01, ∗∗q < 0.001. Only species with significant country or geographic associations were included in correlations involving these.