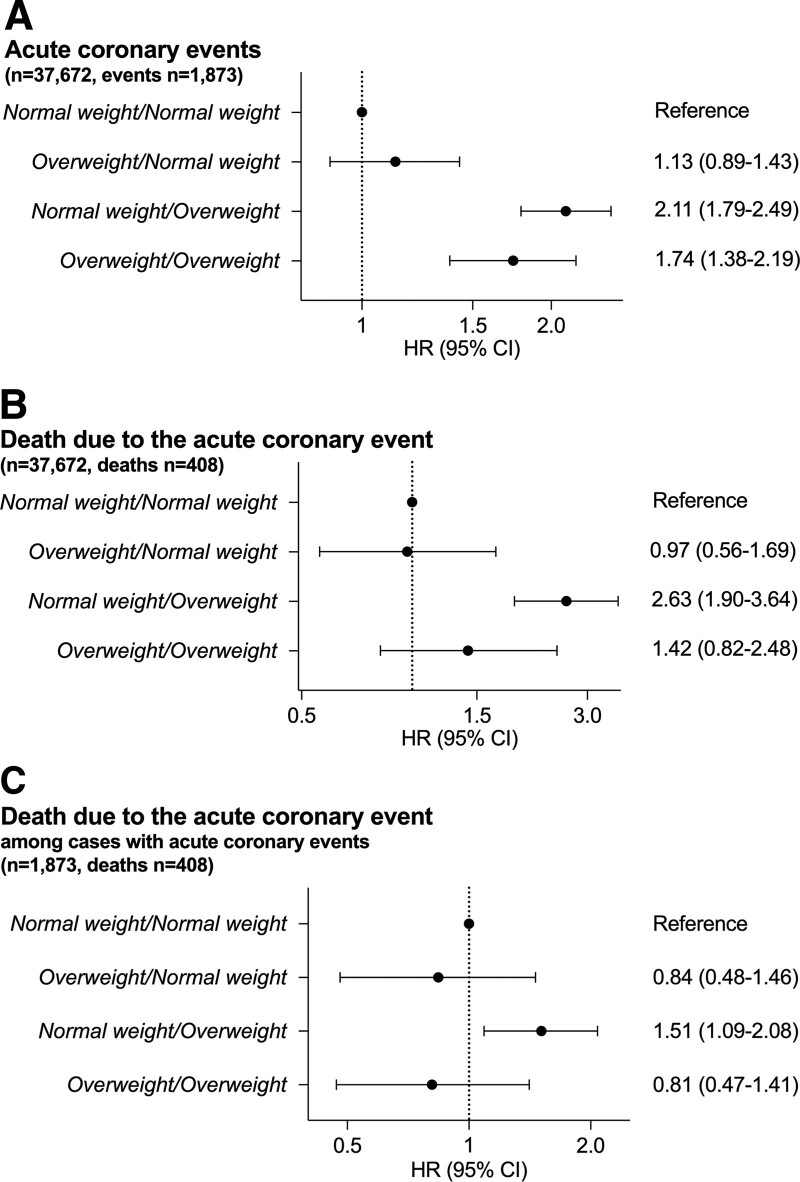
Figure 3.
Associations between childhood and young adult overweight groups and the risk of adult acute coronary events and death due to the event in the BEST (BMI Epidemiology Study) Gothenburg cohort. A, Acute coronary events: hazard ratios (HRs) for the risk of an acute coronary event in the complete cohort (n=37 672) were calculated using Cox proportional hazards regression adjusted for birth year and country of birth. Normal weight/normal weight (=reference; normal weight at both 8 and 20 y of age) n=33 514 (event cases: 1573), overweight/normal weight (overweight at 8, normal weight at 20) n=1368 (70), normal weight/overweight (normal weight at 8, overweight at 20) n=1800 (156), overweight/overweight (overweight at both 8 and 20 y of age) n=990 (74). B, Death due to the acute coronary events: HRs for the risk of death due to the acute coronary event in the complete cohort (n=37 672) were calculated using Cox proportional hazards regression adjusted for birth year and country of birth. Normal weight/normal weight (=reference) n=33 514 (341 died), overweight/normal weight n=1368 (13 died), normal weight/overweight n=1800 (41 died), overweight/overweight n=990 (13 died). C, Death due to the acute coronary event among individuals with an acute coronary event: HRs for the risk of death due to the acute coronary event among individuals with an acute coronary event (n=1873) were calculated using Cox proportional hazards regression adjusted for birth year and country of birth. Normal weight/normal weight n=1573 (=reference; 341 died), overweight/normal weight n=70 (13 died), normal weight/overweight n=156 (41 died), overweight/overweight n=74 (13 died). Childhood overweight at 8 y of age24 was defined as body mass index (BMI) ≥17.9 kg/m2 while young adult overweight at 20 y of age was defined as BMI ≥25 kg/m2. All models have been adjusted for birth year and country of birth.