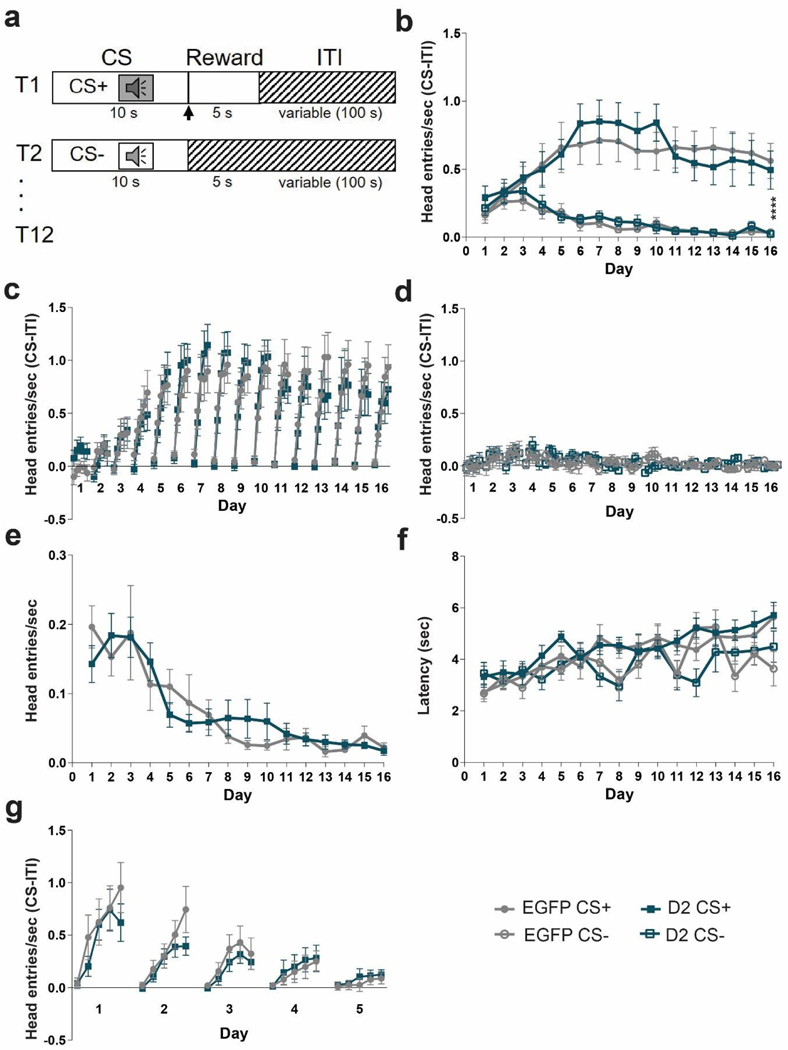
Figure 3. D2R overexpression does not impair Pavlovian learning.
(a) Task design. Mice are trained with 24 (12 CS+, 12 CS-) trials /day for 16 days. Each trial starts with a 10 sec tone (CS+ or CS-). At the end of the CS+ a dipper comes up presenting milk as a food reward for 5 sec. There is an intertrial interval (ITI) variable in length (100 sec). (b) To determine learning, anticipatory responses (head entries/sec (CS-ITI)) were measured. Anticipatory head entries during the CS+ increased for both EGFPNAcInd (filled light circles) and D2R-OENAcInd (filled dark squares) mice and decreased during the CS-for both EGFPNAcInd (open light circles) and D2R-OENAcInd (open dark squares) mice. Both groups learned to distinguish the CS+ and CS-(****p< 0.0001). There was no effect of genotype on learning over the 16 days of training (p= 0.9977). (c) Within each day, the 10 sec CS+ was split into 5 two-second time bins to better visualize the anticipatory response. EGFPNAcInd (filled light circles) and D2R-OENAcInd (filled dark squares) sharply increased head entries into the reward port across the 10 sec CS+ (p< 0.0001) and continued this anticipatory behavior across the 16 days of training (p< 0.0001). There was no effect of genotype on learning (p= 0.9375). (d) EGFPNAcInd (open light circles) and D2R-OENAcInd (open dark squares) showed no anticipatory response during the 10 sec CS-. There was no effect of genotype on learning (p= 0.9988). (e) Head entries during the ITI decreased over the 16 days of training comparably for both groups with no difference between groups (p= 0.6173). (f) Latency for the first head entry during the CS+ and CS-increased for EGFPNAcInd (filled light circles/open light circles) and D2R-OENAcInd (filled dark squares/open dark squares). There was no difference between groups. (g) Anticipatory response to the CS+ attenuated over 5 days of extinction learning. Both groups similarly decreased anticipatory head entries during the CS+ (p< 0.0001). There was no difference in extinction learning between the two groups (p= 0.5247). Data from 8 or 16 animals per genotype was used to calculate all statistics reported.