Figure 1.
3-Dimensional Solid Printouts and Virtual Heart Models
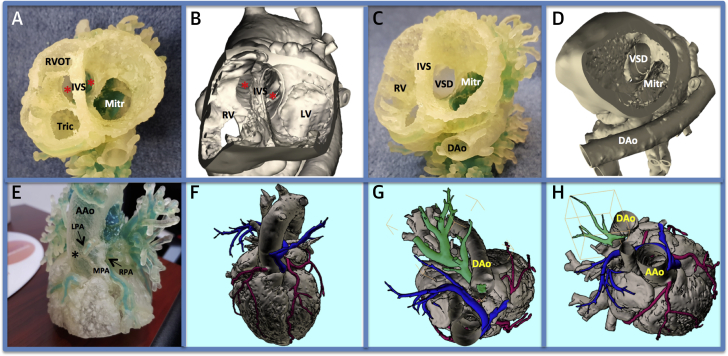
(A) A comparison of the 3-dimensional (3D) printed heart model and (B) the virtual 3D reconstruction model. The model is cut at the midventricular level with a viewpoint toward the base of the heart, which allows optimal visualization of the over-riding aorta (asterisks). The hypoplastic right ventricular outflow tract (RVOT) is also visible. (C and D) A tangential view from the left clearly reveals the ventricular septal defect (VSD) and its relationship with the mitral orifice. (E and F) A solid printout of the personalized 3D heart model, anterior view. A central shunt (asterisk) connects the ascending aorta (AAo) with the hypoplastic pulmonary artery (MPA). The right pulmonary artery (RPA) and left pulmonary artery (LPA) are also hypoplastic, and their course can be followed (displayed in blue) in the virtual model. The coronary arteries are displayed in red. (G and H) The 3D virtual model with different off-axis cut planes. Several major aortopulmonary collateral arteries are displayed in green, with clear appreciation of their origin from the descending aorta. See Videos 1 and 2. Dao = descending aorta; IVS = interventricular septum; LV = left ventricle; Mitr = mitral orifice; RV = right ventricle; Tric = tricuspid orifice.