Figure 5.
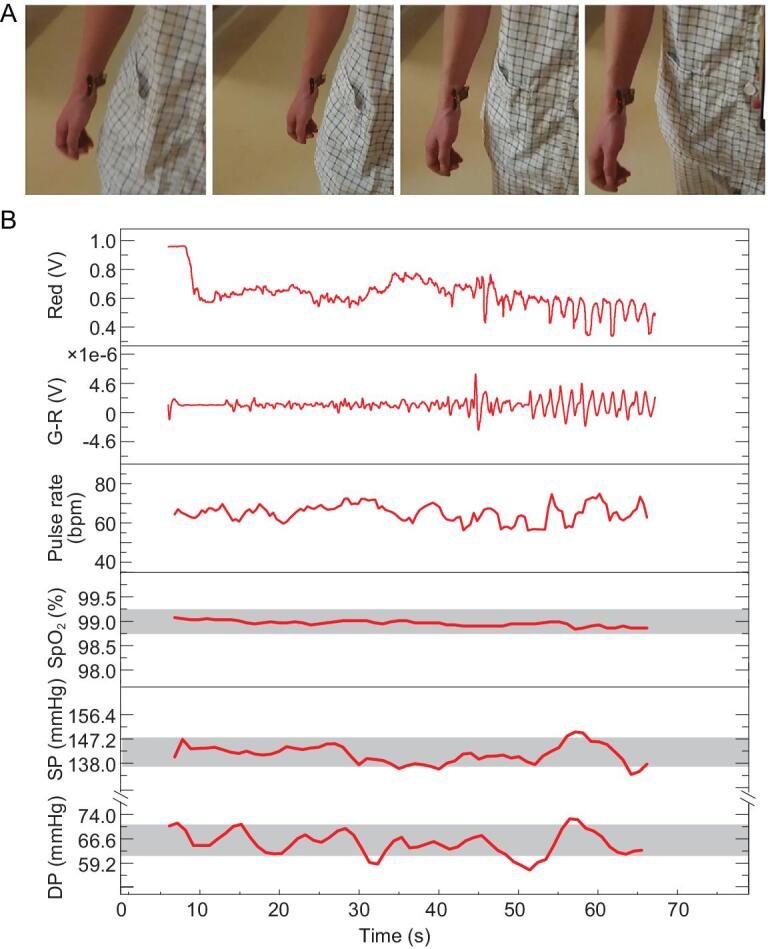
Skin-like systems mounted on the wrist to detect the subject's physiological information while walking. (A) Images of the subject's wrist to which were attached the skin-like systems during walking. The skin-like systems were smeared by optical filter dye to limit the ambient light interference. (B) The signal of original PPG, optical difference, pulse rate, SpO2 and blood pressure monitoring during subject walking. Grey blocks: ±0.5% and ±10 mm Hg error.
