Figure 2.
Phylogenetic analyses, PCA and admixture analyses based on nuclear genome sequences. (a) NJ phylogeny of 74 Malayan pangolins (MJ) (5 samples with known geographic sources; * Yunnan, 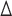 Myanmar, + Malaysia). ML phylogeny produced similar results and is shown as a small version to the right of the figure as a sub-figure. Two populations (MJA and MJB) and subpopulations within the two populations (MJA1-2 and MJB1-3) are labeled. MJA1 and MJA2 are also shown as a magnified version in the top-left of the figure. The values around the black point represent bootstrap support. (b) NJ phylogeny of 23 Chinese pangolins (MP) (9 samples with known geographic sources; * Yunnan, o Taiwan island). ML phylogeny produced similar results and is shown as a small version to the right of the figure as a sub-figure. Two populations (MPA and MPB) are labeled. The values around the black point represent bootstrap support. (c) Principal component analysis (PCA) for 74 MJ individuals. PCA for the MJA population is also shown. (d) PCA for 23 MP individuals. (e) Admixture analyses for 74 MJ individuals. The postulated number of ancestral clusters (K) was set from 2 to 5. (f) Admixture analyses for 23 MP individuals. The postulated number of ancestral clusters (K) was set from 2 to 5.
Myanmar, + Malaysia). ML phylogeny produced similar results and is shown as a small version to the right of the figure as a sub-figure. Two populations (MJA and MJB) and subpopulations within the two populations (MJA1-2 and MJB1-3) are labeled. MJA1 and MJA2 are also shown as a magnified version in the top-left of the figure. The values around the black point represent bootstrap support. (b) NJ phylogeny of 23 Chinese pangolins (MP) (9 samples with known geographic sources; * Yunnan, o Taiwan island). ML phylogeny produced similar results and is shown as a small version to the right of the figure as a sub-figure. Two populations (MPA and MPB) are labeled. The values around the black point represent bootstrap support. (c) Principal component analysis (PCA) for 74 MJ individuals. PCA for the MJA population is also shown. (d) PCA for 23 MP individuals. (e) Admixture analyses for 74 MJ individuals. The postulated number of ancestral clusters (K) was set from 2 to 5. (f) Admixture analyses for 23 MP individuals. The postulated number of ancestral clusters (K) was set from 2 to 5.

