Table 2. Results of the Optimization of Lovastatin Crystal Yield, YAPI, for Five Crystallization Methods—Cooling Crystallization with: Only Pure Solvent Allowed in the Initial State (CP), Mixtures Allowed Throughout (CM); Antisolvent Crystallization with: Only Pure Solvent Allowed in the Initial State (ASP), Mixtures Allowed Throughout (ASM); and Hybrid Cooling and Antisolvent Crystallization (H)a.
| solvents |
||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| method | rank | YAPI/% | χs/(g/g) | T0/K | s1 | s2 | ||||
| cooling (CP) | 1 | 97.47 | 73.02 | 361.15 | 1.000 | 1.000 | n-heptane | |||
| 2 | 96.33 | 3.50 | 368.75 | 1.000 | 1.000 | isobutyl acetate | ||||
| 3 | 94.89 | 3.50 | 363.35 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1-pentanol | ||||
| 4 | 93.46 | 4.11 | 356.35 | 1.000 | 1.000 | isopropyl acetate | ||||
| 5 | 92.75 | 3.50 | 357.05 | 1.000 | 1.000 | butyl acetate | ||||
| cooling (CM) | 1 | 97.47 | 73.02 | 361.15 | 1.000 | 1.000 | n-heptane | |||
| 2 | 96.45 | 3.50 | 369.15 | 0.962 | 0.962 | isobutyl acetate | n-pentane | |||
| 3 | 94.89 | 3.50 | 363.35 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1-pentanol | ||||
| 4 | 93.46 | 4.11 | 356.35 | 1.000 | 1.000 | isopropyl acetate | ||||
| 5 | 93.36 | 3.50 | 358.25 | 0.915 | 0.915 | butyl acetate | n-pentane | |||
| anti-solvent (ASP) | 1 | 92.16 | 85.84 | 293.15 | 1.000 | 0.158 | methyl acetate | n-heptane | ||
| 2 | 90.24 | 109.56 | 293.15 | 1.000 | 0.165 | ethyl acetate | n-heptane | |||
| 3 | 89.85 | 78.01 | 293.15 | 1.000 | 0.134 | methyl acetate | n-pentane | |||
| 4 | 87.22 | 101.97 | 293.15 | 1.000 | 0.139 | ethyl acetate | n-pentane | |||
| 5 | 85.62 | 170.49 | 293.15 | 1.000 | 0.174 | propyl acetate | n-heptane | |||
| anti-solvent (ASM) | 1 | 93.04 | 75.80 | 293.15 | 0.928 | 0.157 | methyl acetate | n-heptane | ||
| 2 | 91.67 | 63.10 | 293.15 | 0.882 | 0.133 | methyl acetate | n-pentane | |||
| 3 | 90.24 | 109.56 | 293.15 | 1.000 | 0.165 | ethyl acetate | n-heptane | |||
| 4 | 87.40 | 100.40 | 293.15 | 0.955 | 0.139 | ethyl acetate | n-pentane | |||
| 5 | 85.62 | 170.49 | 293.15 | 1.000 | 0.174 | propyl acetate | n-heptane | |||
| hybrid (H) | 1 | 99.23 | 7.93 | 370.35 | 1.000 | 0.174 | propyl acetate | n-heptane | ||
| 2 | 99.16 | 8.59 | 373.15 | 1.000 | 0.184 | butyl acetate | n-heptane | |||
| 3 | 98.97 | 7.25 | 370.35 | 1.000 | 0.145 | propyl acetate | n-pentane | |||
| 4 | 98.93 | 10.88 | 373.15 | 1.000 | 0.228 | isobutyl acetate | n-heptane | |||
| 5 | 98.90 | 7.77 | 373.15 | 0.954 | 0.154 | butyl acetate | n-pentane | |||
For each method, the top five solvent
mixtures are ranked with respect to the crystal yield of lovastatin
achieved. The solvent consumption, χs, initial temperature, T0, and binary solvent compositions in terms
of initial and final mole fractions of solvent s1,  and
and 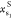 ,
are also given. In all cases, the maximum
allowable temperature is 373.15 K, the minimum solvent mass is 3.5
g solvent/(g crystal), and the final temperature is 293.15 K.
,
are also given. In all cases, the maximum
allowable temperature is 373.15 K, the minimum solvent mass is 3.5
g solvent/(g crystal), and the final temperature is 293.15 K.
