Fig. 1.
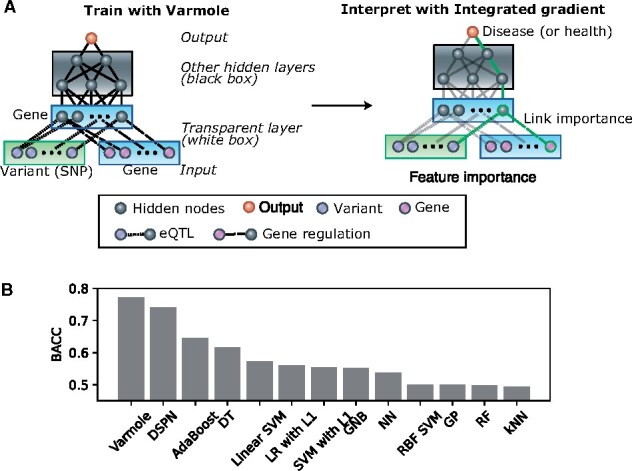
Varmole, a biologically drop-connect deep neural network model for prioritizing disease risk variants and genes. (A) Varmole model has four major layers: (i) the input layer consists of SNPs and genes; (ii) a transparent layer duplicating the gene nodes in the input layer; (iii) hidden layer(s); (iv) the phenotype layer as output. The prior biological networks from eQTLs and GRNs link SNPs/genes to genes from the input layer to the transparent layer, which enables biological drop-connect. Varmole can be evaluated by BACC and prioritizes the genes, SNPs and links for a phenotype (e.g. green path) using the integrated gradients. (B) Classification performance comparison by the BACC between Varmole and other state-of-the-art methods for genotype-phenotype prediction. The BACC is defined by BACC where TP, TN, FP, FN are true positive, true negative, false positive and false negative, respectively
