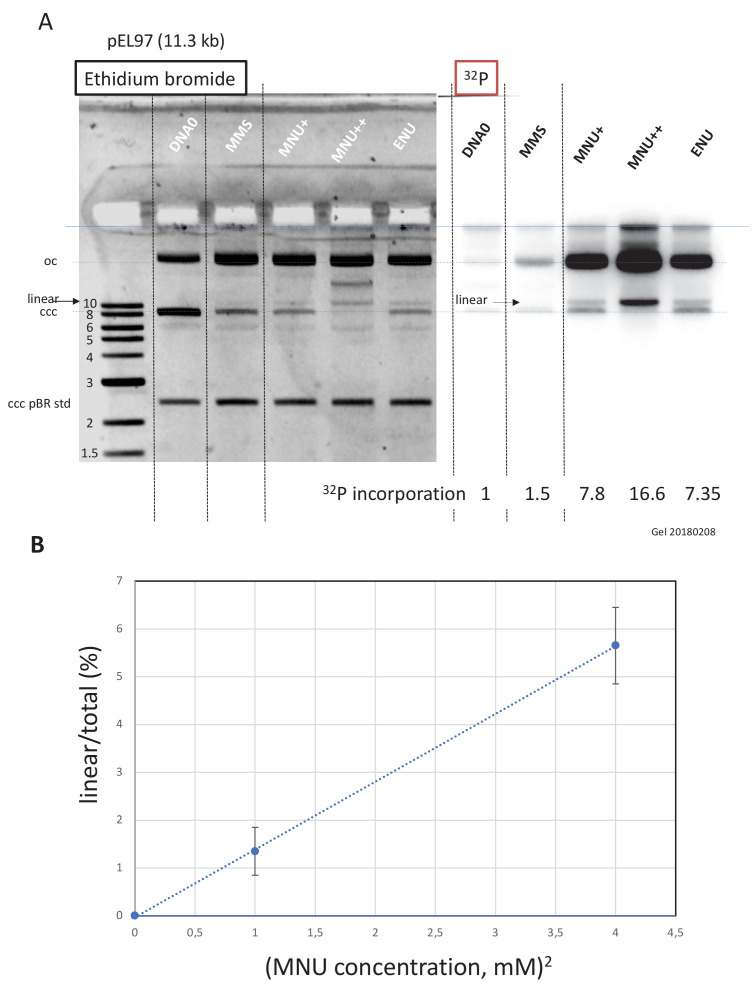
Figure 4. Double-strand breaks occur in MNU-treated plasmids during incubation in extracts.
(A) Analysis by agarose gel electrophoresis (AGE) of alkylated plasmids (pEL97: 11.3 kb) incubated in nucleoplasmic extracts (NPE) in the presence of α32P-dATP. Plasmid pEL97 was treated with methyl-methane sulfonate (MMS), N-methyl-N-nitrosourea (MNU)+, and ENU as to introduce ≈ one alkylation event, on average, every 500 nt. For MNU, a plasmid with twice the level of alkylation (MNU++, one lesion every 250 nt) was also produced (Figure 4—figure supplement 1). Alkylation of these plasmids essentially not affected their migration on agarose gels (Figure 4—figure supplement 2A). After 2 hr of incubation, the reaction was stopped and a known amount of pBR322 (10 ng) plasmid was added as an internal standard. Ethidium bromide image: in different lanes, the internal standard band, pBR (covalently closed circular [ccc]), appears to be of similar intensity (1158 +/- 95 arbitrary units [AU]), assessing reproducible DNA extraction. For the alkylated plasmids, incubation in NPE led to massive conversion from ccc to relaxed plasmids. 32P image: little incorporation of 32P-dATP is seen in DNA0 and in MMS-treated plasmids compared to MNU- and ENU-treated plasmids as shown by the relative incorporation levels normalized to one for untreated plasmid (DNA0). As expected, the MNU++ sample exhibits about twice the amount of incorporated radioactivity compared to MNU+. In both ethidium bromide and 32P images, a small amount of linear plasmid is seen mostly in the MNU++ sample. This band is also visible in the MNU+ and ENU lanes although at a weaker intensity. (B) Quadratic dose-response for double-strand break (DSB) formation. When the % of linear form (linear/(linear + oc)) is plotted as a function of the square dose of MNU (mM2) for untreated, MNU+, and MNU++ plasmids, we observed a straight line (y = 1.4173x - 0.0288; R² = 0.9999).