Figure 2.
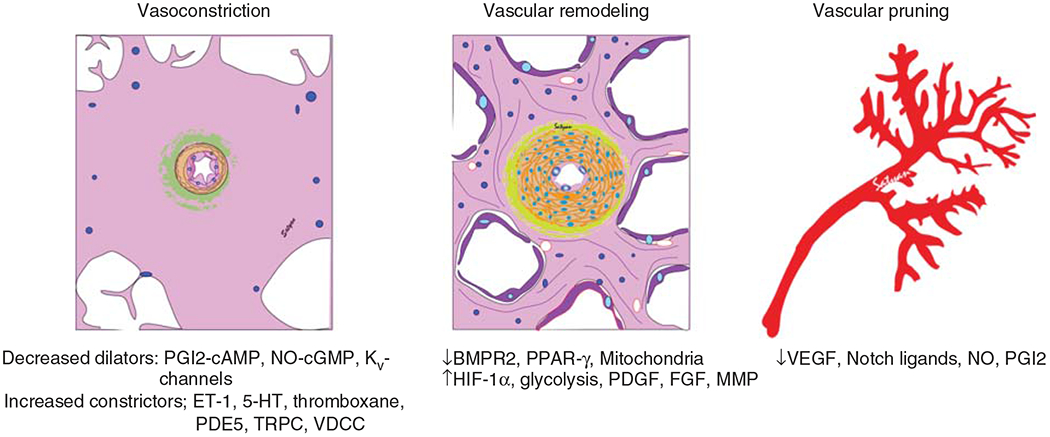
Molecular and structural mechanisms of pulmonary vascular disease. PGI2, prostacyclin; NO, nitric oxide; sGC, soluble guanylate cyclase; cAMP, cyclic adenosine monophosphate; cGMP, cyclic guanosine monophosphate; PDE, phosphodiesterase; Kv channel, voltage-gated potassium channel; ET-1, endothelin-1; 5HT, 5-hydroxytryptamine; TRPC, transient receptor potential cation channel; VDCC, voltage-dependent calcium channel; BMPR2, bone morphogenetic protein receptor-2; PPAR-γ, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ; PDGF, platelet-derived growth factor; FGF, fibroblast growth factor; MMP, matrix metalloproteinase; HIF-1α, hypoxia inducible factor-1α VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor.
