Figure 1.
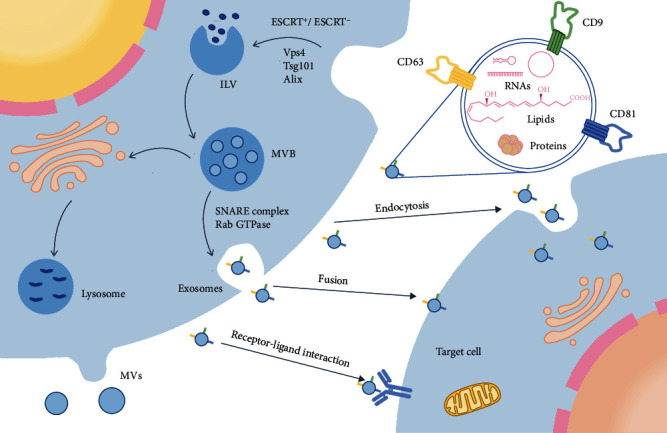
Biogenesis and cellular uptake of exosomes. The plasma membrane invaginates through the ESCRT-dependent and ESCRT-independent pathways to form ILVs. Late endosomes containing ILVs are called multivesicular bodies (MVBs). Some MVBs are transported to the Golgi complex circulation and finally transported to the lysosome for degradation, and some MVBs are fused with the plasma membrane under the influence of the Rab family, SNARE complex, and tubulin before being released from the cell. Exosomes released from cells can enter target cells through fusion, receptor-mediated endocytosis, macrophage phagocytosis, or phagocytosis. The surfaces of exosomes contain many molecules. This figure shows three common molecules (CD9, CD63, and CD81) on the surface of MSC-EXs.
