Figure 6.
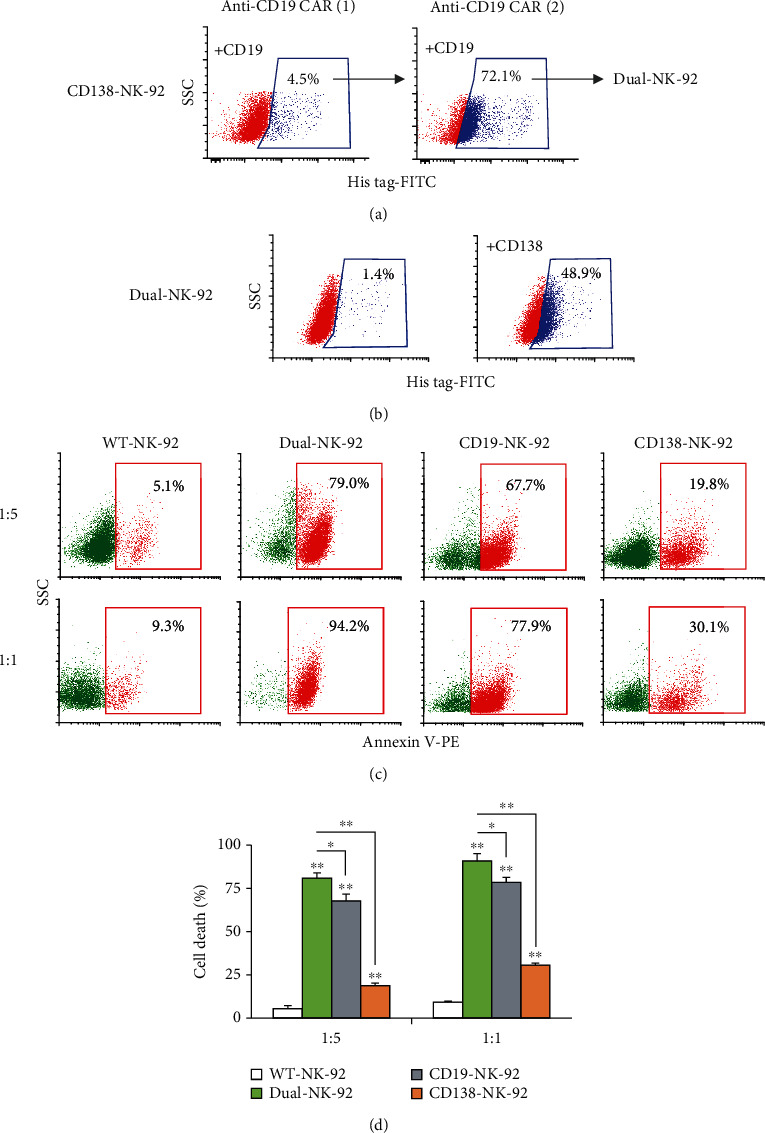
Generation of dual CD19/CD138-NK-92 cells and its cytotoxicity against ALL cells expressing both CD19 and CD138 antigens. (a) Stable CD138-NK-92 cells were subjected to multiple rounds of lentiviral transduction of anti-CD19-CAR and sequential FACS enrichment based on CD19 antigen-binding activity to obtain dual-NK-92 cells. (b) Anti-CD138-CAR expression in dual-NK-92 cells, as evaluated by flow cytometry based on its antigen-binding activity to His tag-rhCD138. (c) Human ALL-derived REH cells were labeled with PKH67 dye; incubated with WT-NK-92, dual-NK-92, CD19-NK-92, or CD138-NK-92 cells at the E : T ratio of 1 : 5 or 1 : 1 for 4 h; and stained with Annexin V-PE. Representative flow cytometric dot plots of Annexin V-positive cells (red box) in PKH67-labeled cells were shown. (d) Percentage of REH cell death was plotted. Data are mean ± s.d. (n = 3). ∗p < 0.05 and ∗∗p < 0.01 versus WT-NK-92 cells or dual-NK-92 cells as indicated; two-sided Student's t-test.
