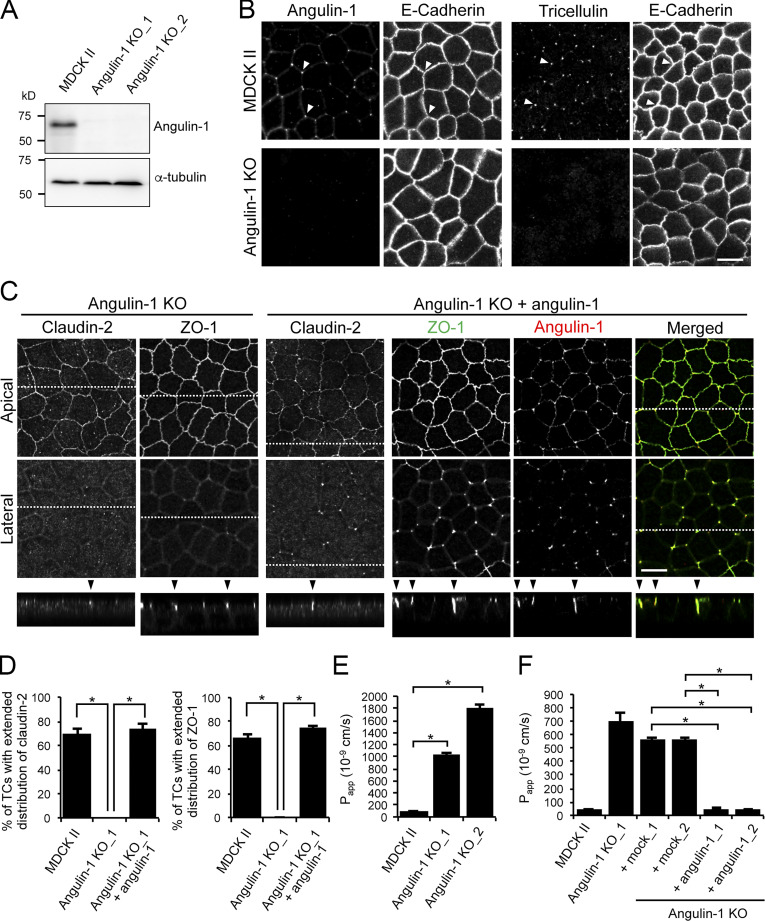
Figure 4.
Role of angulin-1 in the localization of TJ proteins at TCs and epithelial barrier function. (A) Western blotting of lysates of MDCK II cells and two independent angulin-1–KO cell clones (angulin-1–KO_1 and –KO_2) with anti–angulin-1 pAb or anti–α-tubulin mAb. (B) Double-immunofluorescence staining of MDCK II cells and angulin-1–KO cells with anti–angulin-1 pAb and anti–E-cadherin mAb or anti-tricellulin pAb and anti–E-cadherin mAb. Arrowheads indicate TCs. (C) Immunofluorescence staining of angulin-1–KO cells and angulin-1–KO cells expressing exogenous angulin-1 (angulin-1–KO + angulin-1). Angulin-1–KO cells were immunostained with anti–claudin-2 mAb or anti–ZO-1 mAb. Angulin-1–KO cells expressing exogenous angulin-1 were singly immunostained with anti–claudin-2 mAb or doubly stained with anti–ZO-1 mAb and anti–angulin-1 pAb. Confocal sections of the apical region, including TJ markers and the lateral region, together with the corresponding Z-stack images along the white dotted lines are shown. Arrowheads indicate TCs. (D) Quantification of TCs with extended distribution of fluorescence signals of claudin-2 and ZO-1 to the basal direction. (E) Paracellular flux of fluorescein in MDCK II cells and two independent angulin-1–KO cell clones (angulin-1–KO_1 and –KO_2). Papp, apparent permeability. (F) Paracellular flux of fluorescein in MDCK II cells, angulin-1–KO cells, two independent mock-transfected angulin-1–KO cell clones (+mock_1 and +mock_2), and two independent angulin-1–KO cell clones expressing exogenous angulin-1 (+angulin-1_1 and +angulin-1_2). Data are shown as mean ± SD (n = 3) and were analyzed by Tukey-Kramer test (D and F) or Dunnett’s test (E). *, P < 0.01. Bars: 10 µm.