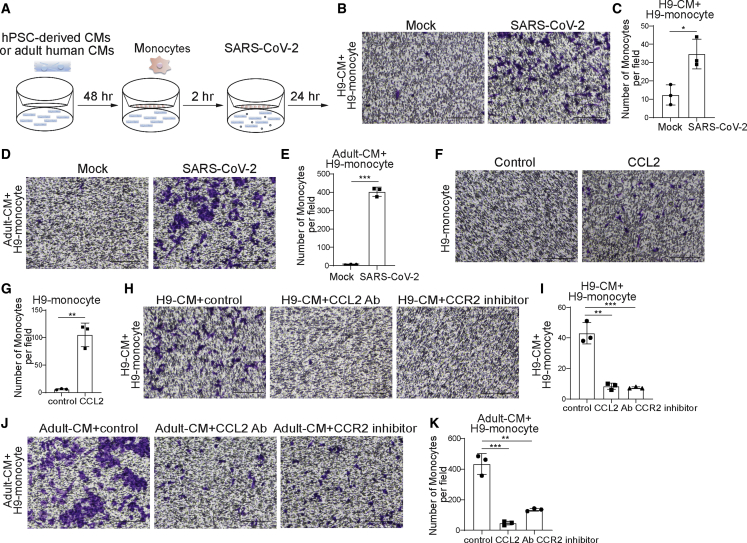
Figure 6.
CMs recruit monocytes following SARS-CoV-2 infection through secreting CCL2
(A) Scheme of the monocyte recruitment assay using hPSC-derived CMs or adult human CMs and hPSC-derived monocytes in the presence of SARS-CoV-2 infection
(B and C) Phase contrast images (B) and quantification (C) of migrated H9-derived monocytes recruited by H9-derived CMs infected with SARS-CoV-2 virus or mock infected in the monocyte migration assay (MOI = 0.1, n = 3 independent experiments). Scale bar, 100 μm.
(D and E) Phase contrast images (D) and quantification (E) of H9-derived monocytes recruited by adult human CMs infected with SARS-CoV-2 virus or mock infected in the monocyte recruitment assay (MOI = 0.1, n = 3 independent experiments). Scale bar, 100 μm.
(F and G) Phase contrast images (F) and quantification (G) of migrated H9-derived monocytes recruited by CCL2 in the monocyte recruitment assay (n = 3 independent experiments). Scale bar, 100 μm.
(H and I) Phase contrast images (H) and quantification (I) of migrated H9-derived monocytes recruited by H9-derived CMs infected with SARS-CoV-2 virus and treated with CCL2-neutralizing antibody or CCR2 inhibitor (RS504393) in the monocyte recruitment assay (MOI = 0.1, n = 3 independent experiments). Scale bar, 100 μm.
(J and K) Phase contrast images (J) and quantification (K) of migrated H9-derived monocytes recruited by adult human CMs infected with SARS-CoV-2 virus and treated with CCL2-neutralizing antibody or CCR2 inhibitor in the monocyte recruitment assay (MOI = 0.1, n = 3 independent experiments). Scale bar, 100 μm.
Data are presented as mean ± SD. p values were calculated by unpaired two-tailed Student’s t test. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001.
See also Figures S4 and S5.