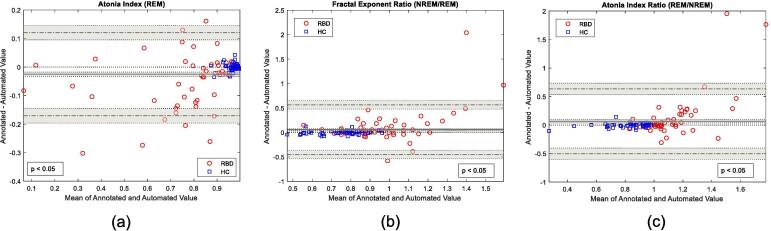
Fig. 5.
Bland and Altman plots of important rapid-eye movement (REM) sleep behaviour disorder (RBD) metrics comparing scores derived from manually and automatically annotated sleep stages. These included the (a) atonia index during REM sleep, (b) atonia index ratio between REM and Non-REM (NREM), and the (c) fractal exponent ratio between REM and NREM. In all cases we can observe that metrics are within the limits of agreement (Bland and Altman, 1986). The p-value (p) details the Kolmogorov-Smirnov test to determine if the difference between metrics calculated from manual and automatic sleep staging are from a normal distribution (rejected when < 0.05). For metrics shown above, the line of equality (the dotted line at zero) does not fall within the limits of confidence around the mean difference (shaded grey area). Therefore when using automated sleep staging the calculated metrics for RBD detection slightly shifts towards values associated with RBD or healthy control (HC) participants. This is unsurprising given misclassification from automated sleep staging will have an impact on the calculation of these metrics.