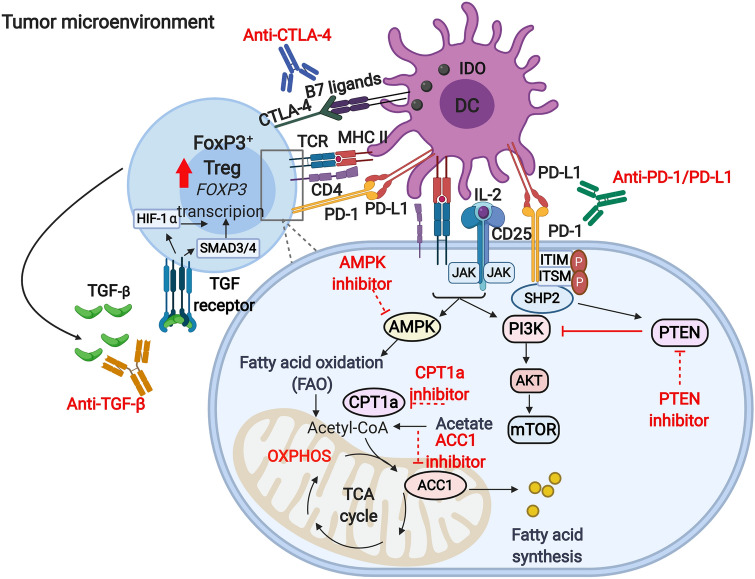
Fig. 2.
Strategies for targeting Treg metabolism. The accumulation of high numbers of Tregs within the tumor microenvironment could be governed by the action of various mediators and signaling pathways. Direct interactions between tolerogenic DCs and Tregs results in the activation of TCR-mediated signaling pathway. Moreover, the interactions between CTLA-4 on Tregs and B7 ligands on DCs induces IDO expression, an enzyme which facilitates tryptophan catabolism and limits its availability to T effector cells. Metabolites from tryptophan catabolism can be also important for Treg induction and FoxP3 stability (not shown here). IL-2/CD25 signaling is essential for the survival and proliferation of Tregs, as it leads to the downstream activation of PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling and STAT5 signaling. PD-1/PD-L1 signaling, on the other hand, suppresses the activation of PI3K/AKT/mTOR via PTEN, thereby favoring FoxP3 expression and stability. TCR-mediated signaling in cooperation with IL-2 signaling triggers the activation of AMPK, a critical protein kinase for lipid metabolism and FAO, which are required for energy production, and Treg survival and function. ACC1 is an enzyme which facilitates fatty acid synthesis, while CPT1a is responsible for FAO. Activated, highly immunosuppressive Tregs can release high levels of TGF-β, which is a key mediator for Treg survival, function and differentiation. Via an autocrine signaling, the activation of TGF-β signaling in Tregs can induce HIF-1α expression and trigger the activation of SMAD3 and 4 signaling, which subsequently prompt FoxP3 expression and Treg function. Targeting PD-1 and CTLA-4 signaling by mAbs could be beneficial in reducing FoxP3 stability and diminishing Treg numbers. Small molecule inhibitors targeting PTEN, ACC1 and CPT1a could offer a therapeutic benefit in cancer by destabilizing FoxP3 expression and suppressing Treg function. Moreover, the neutralization of TGF-β could block the HIF-1 and SMAD-mediated FoxP3 induction, and the inhibition of AMPK activity could be beneficial in depleting Tregs and disrupting FoxP3 expression. Potential therapeutic inhibition strategies are indicated by dotted red lines