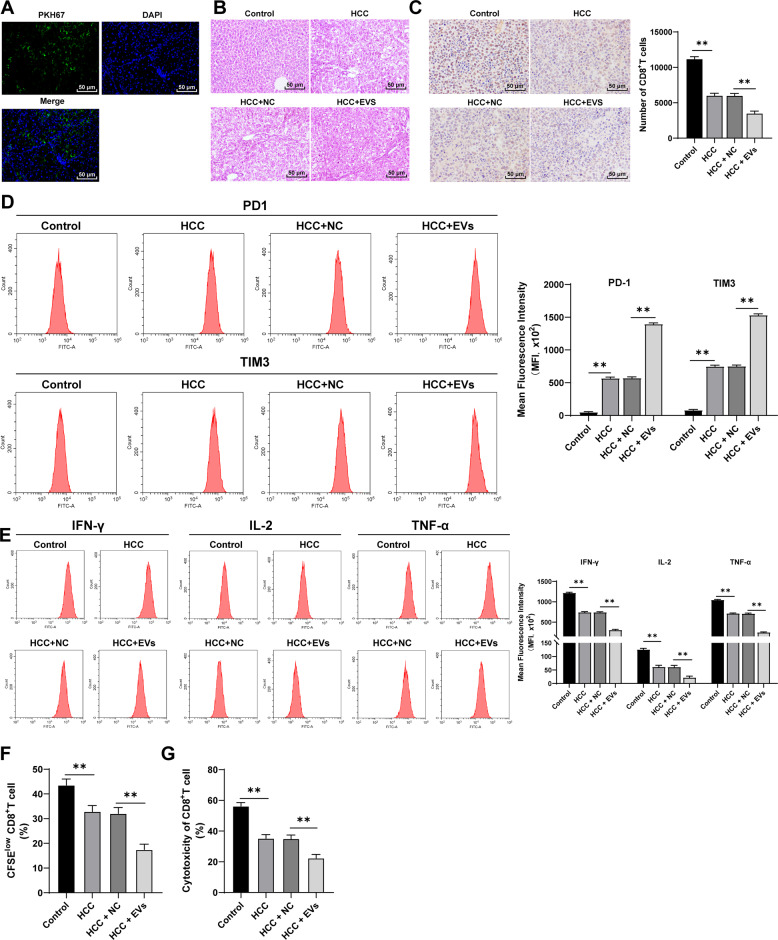
Fig. 1. M2 macrophage-derived EVs promoted CD8+ T cell exhaustion in mice with primary HCC.
The murine model of primary HCC was established by DEN/CCl4 combined induction, and the model mice were injected with EVs via tail vein. A The absorption of EVs by mouse liver tissues was detected using immunofluorescence. Green indicated PKH67-labeled EVs and blue indicated nuclear staining. B Histopathological changes of liver tissues were observed using HE staining at the 40th week after induction. C The number of CD8+ T cells in tumor sections was detected using immunohistochemistry. PBMCs were isolated from the mouse liver and CD8+ T cells were sorted. D The expressions of immune checkpoint inhibitory receptors (PD1 and TIM3) on CD8+ T cells were detected using flow cytometry. E The expressions of effector cytokines (IFN-γ, IL-2, and TNF-α) were detected using flow cytometry. F The proliferation ability of CD8+ T cells was measured using flow cytometry. G The ability of CD8+ T cells to kill Hep1-6 cells was measured using flow cytometry. N = 6. The cell experiment was repeated 3 times. Data are presented as mean ± standard deviation and analyzed using one-way ANOVA, followed by Tukey’s multiple comparison test, **p < 0.01.