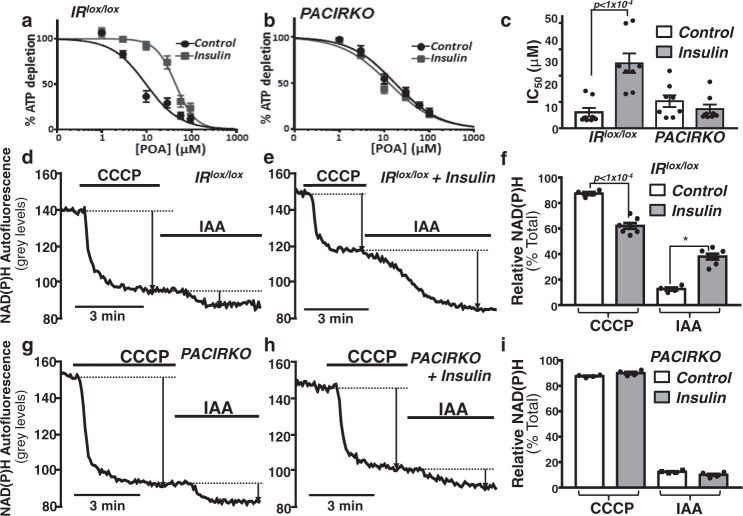
Fig. 7. Insulin-mediated protection of POA-induced ATP depletion and switch from mitochondrial metabolism to glycolysis was abolished in PACIRKO mice.
POA concentration-response curves for ATP depletion in the absence and presence of insulin (10 nM) in pancreatic acinar cells isolated from IRlox/lox (a) and PACIRKO mice (b) and corresponding mean IC50 values (±SEM) (c). Mean data are from eight separate experiments. Significance (exact p values as indictated) was determined by repeated measures one-way ANOVA with Sidak’s multiple comparisons. NADH autofluorescence was used to assess the relative mitochondrial vs glycolytic metabolism in pancreatic acinar cells isolated from IRlox/lox (d, e) and PACRIKO mice (g, h). Sequential background-subtracted images were acquired every 5 s (500 ms exposure), and changes in NADH autofluorescence were quantified as raw fluorescence grey levels. To determine the relative mitochondrial and glycolytic contributions to NADH autofluorescence, the cells were treated with 4 μM CCCP and then 2 mM iodoacetate (IAA), respectively, and responses were normalised to the total (f, IRlox/lox; i, PACIRKO). Mean data (±SEM) from four separate experiments for each experimental condition, except IRlox/lox with insulin (n = 7). Significance (specifc p values as indicated) was determined by either repeated measures (c) or ordinary one-way ANOVA (f, i) with Sidak’s multiple comparisons.