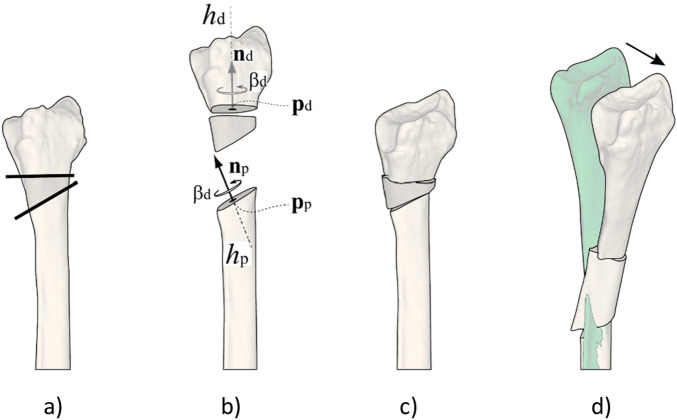
Figure 1.
(a) Rotational alignment correction of a deformed bone using an oblique double-cut rotation osteotomy. (b) The distal segment is rotated over βd about the axis (hd) oriented in the direction of the cutting plane normal (nd) and a point on the axis (pd), being the centroid of the polygon points in the cutting plane. A second axis (hp) is defined in the same way using the proximal cutting plane (cutting plane normal np, point on the axis pp). The rotated distal segment and the middle segment are considered a single assembly which is rotated about the axis over the angle βp. The exploded view shows applicable parameters. (c) Aligned bone segments after rotation. (d) In general, a residual translation error may persist (arrow) between the corrected bone and the target bone (green), although rotational alignment is achieved. This translation error depends on the chosen osteotomy parameters, such as the osteotomy plane locations.