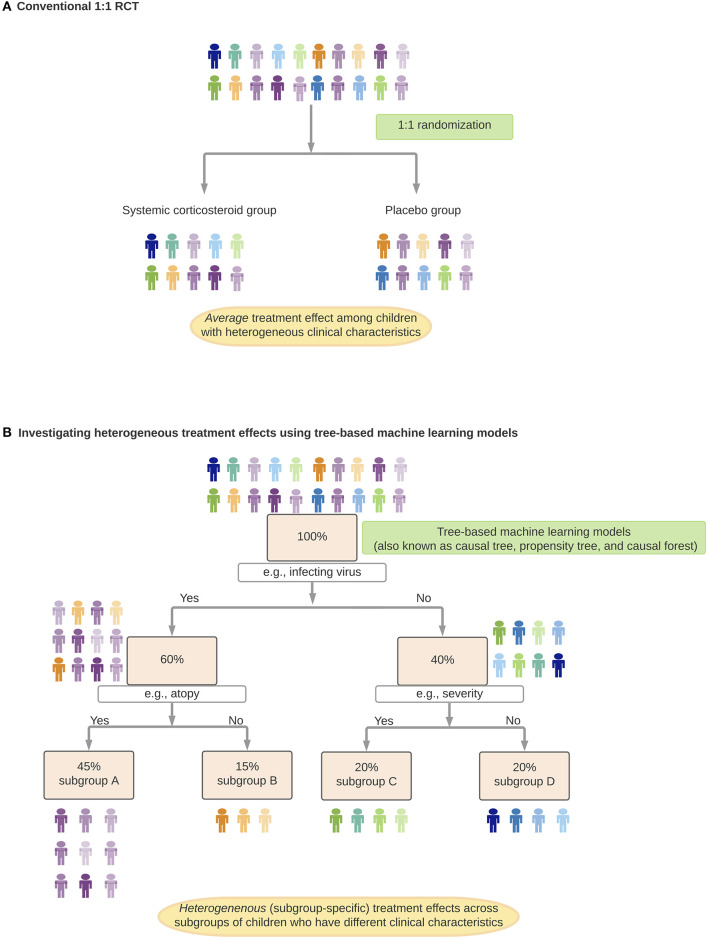
Figure 2.
Identification and estimation of heterogenous treatment effects. In this hypothetical example, suppose, we investigate treatment effects of systemic corticosteroids on hospitalization rates among preschool children with virus-induced wheezing. (A) Randomized control trial (RCT) to investigate the average treatment effect of systemic corticosteroids (conventional 1:1 RCT). (B) Investigating heterogeneous treatment effects using tree-based machine learning models. In each of the branches (e.g., subgroup A children have specific virus infection and a history of atopy), children have a comparable predicted probability of receiving systemic corticosteroids. Children within each subgroup function as if they came from an RCT with eligibility criteria stratified by clinical characteristics.