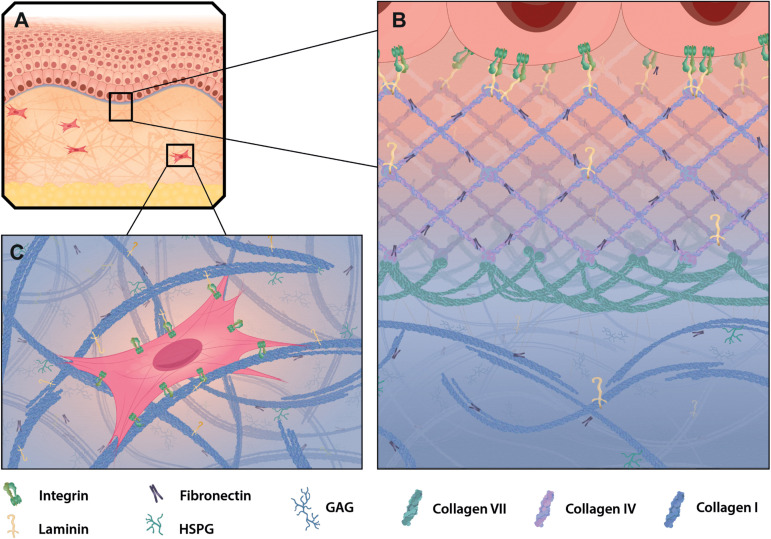
FIGURE 3.
ECM in healthy mammalian skin. (A) Skin is composed of the epidermis (top part), dermis (mid part) and adipose cell-rich hypodermis (lower part) and resembles a highly accessible model tissue to study epithelia, connective tissue and extracellular matrix (ECM) structures specific for those layers. The BM (purple) connects the epidermis to the dermis, which is comprised of interstitial matrix. (B) The dominant structural component in the BM is collagen type IV, which builds a meshwork with interspersed laminin and fibronectin. Together they build the basis for keratinocyte attachment via integrins. Collagen type VII reaches into the papillary dermis and stabilizes the dermal-epidermal junction. (C) In the dermis collagen type I and fibronectin build a fibrillary structure that allows cell adhesion and migration through the matrix. Shown is a fibroblast attaching to collagen and fibronectin via integrins.