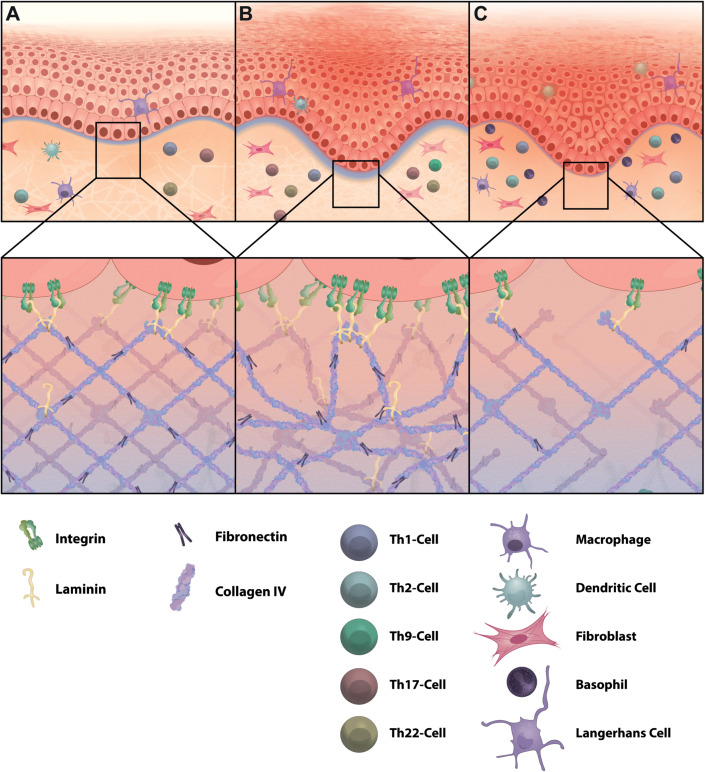
FIGURE 5.
ECM changes in skin inflammation. Inflammatory skin diseases can alter the composition and structure of the ECM. (A) In healthy skin collagen type IV builds a network with interspersed laminin to form the BM. This provides attachment points for basal keratinocytes of the epidermis and forms a protective layer to control leukocyte navigation through adjusted gap sizes and limits entry of harmful invaders via incorporation of sticky PG/GAGs. (B) Psoriasis is defined by high infiltration of IL-17 and IL-22 producing T helper cells. The BM in psoriasis is highly unstructured and thicker compared to healthy skin and shows elevated levels of laminin and fibronectin. (C) In atopic dermatitis, which is a T helper 2-driven inflammatory skin disease, collagen type IV and fibronectin are decreased, resulting in a thinner BM. Increased hyaluronan and MMPs are further characteristic for atopic dermatitis (not illustrated here). Not all relevant immune cells are illustrated.