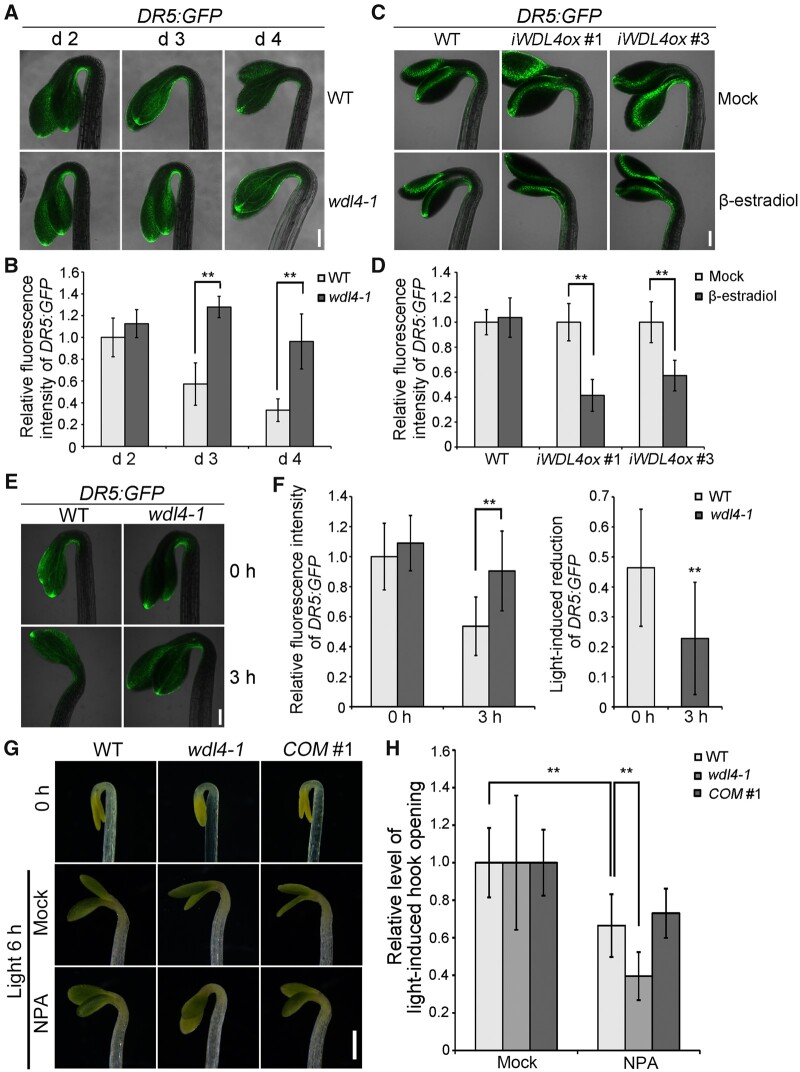
Figure 5.
WDL4 mutation alters auxin maxima and impairs sensitivity to auxin efflux inhibitor during hook development. A and B, Representative images of DR5:GFP expression patterns and quantified fluorescence intensity in the hook region of dark-grown WT and wdl4-1 mutants at different time points. Values in (B) represent mean ± sd (n > 12 independent seedlings; **P < 0.01). Scale bar = 0.2 mm. C and D, Representative images of DR5:GFP expression patterns and quantified fluorescence intensity in the hook region of etiolated seedlings with induced overexpression of WDL4 (iWDL4ox). Seedlings were germinated and grown vertically in the dark for 48 h, and transferred to new plates with or without β-estradiol for another 24 h in the dark. Values in (D) represent mean ± sd (n > 12 independent seedlings; **P < 0.01). Scale bar = 0.2 mm. E and F, Representative images of DR5:GFP expression patterns and quantified fluorescence intensity during light-induced hook opening. WT and wdl4-1 seedlings were germinated and grown vertically in the dark for 42 h, and transferred to white light for another 3 h. Values in (F) represent mean ± sd (n > 15 independent seedlings; **P < 0.01). Scale bar = 0.2 mm. G and H, Representative images and quantified analysis of NPA effect on light-induced hook opening. WT, wdl4-1, and wdl4-1 WDL4pro:WDL4-GFP (COM #1) seedlings were germinated and grown vertically in the dark for 42 h, and transferred to white light for another 6 h with or without NPA treatment. Values in (F) represent mean ± sd (n > 17 independent seedlings; **P < 0.01). Scale bar = 0.5 mm.