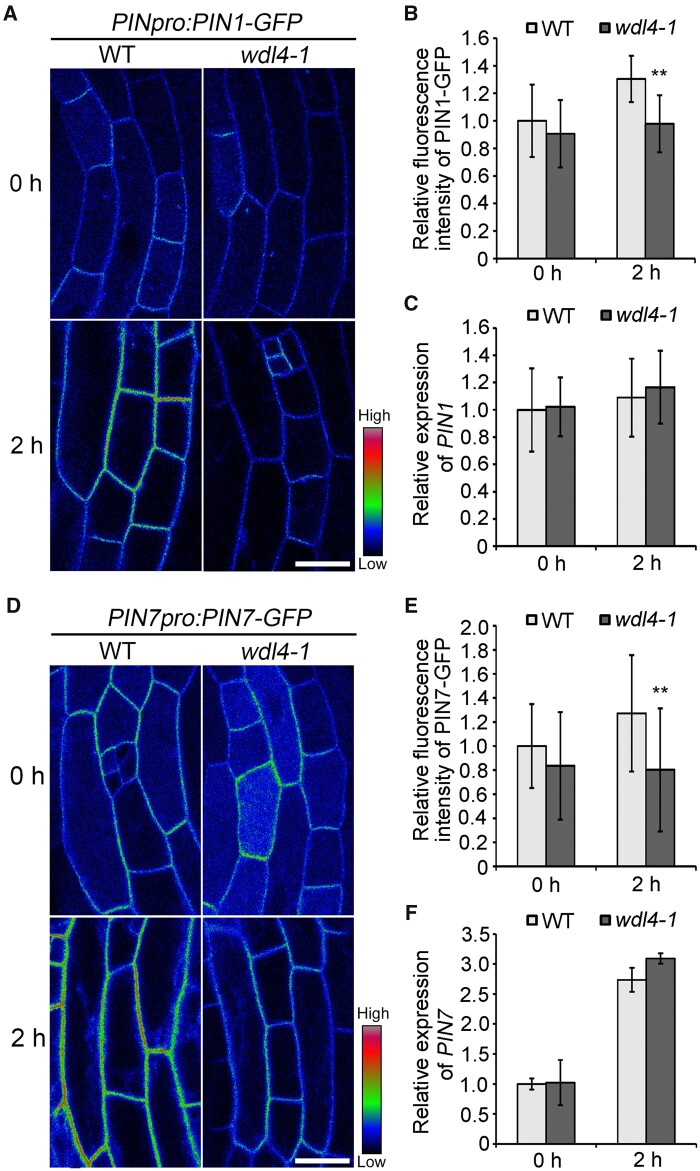
Figure 6.
WDL4 mutation attenuates the enhanced distribution of PIN1–GFP and PIN7–GFP at the PM during light-induced hook opening. A and B, Representative images shown as pseudocolors (red-green-blue palette) and relative fluorescence intensity of PM-localized PIN1–GFP in hook epidermal cells in WT and wdl4-1 seedlings expressing PIN1pro:PIN1-GFP. Seedlings were germinated and grown vertically in the dark for 42 h, and transferred to white light for another 2 h. Values represent mean ± sd (n > 14 independent seedlings; **P < 0.01). Scale bar = 20 μm. C, Relative expression of PIN1 in the apical hook of the seedlings used in A. One to two millimeter of the apical hook regions from seedlings were used for RNA extraction. Values represent mean ± SD for three individual biological repeats. D and E, Representative images shown as pseudocolors and relative fluorescence intensity of PM-localized PIN7–GFP in hook epidermal cells in WT and wdl4-1 seedlings expressing PIN7pro:PIN7–GFP. Seedlings were grown and treated the same way as in A. Values represent mean ± sd (n > 21 independent seedlings; **P < 0.01). Scale bar = 20 μm. F, Relative expression of PIN7 in the apical hook of the seedlings used in D. One to two millimeter of the apical hook regions from seedlings were used for RNA extraction. Values represent mean ± sd for three individual biological repeats.