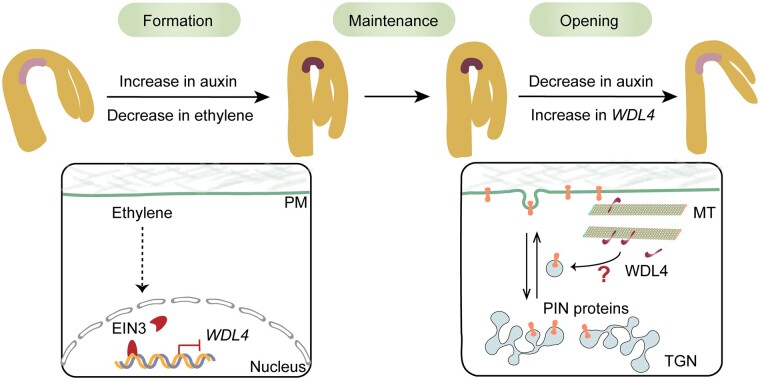
Figure 8.
A hypothetical model for WDL4 function in apical hook development. The formation of hook curvature in etiolated seedlings is achieved by growth inhibition along with asymmetric auxin accumulation at the concave side, while hook opening is achieved by growth promotion and a decrease in the auxin maxima. During the early stage of hook formation, the level of ethylene is high, and the key transcription factor EIN3 accumulates. EIN3 binds to the promoter region of WDL4 and suppresses WDL4 expression. During hook opening, when ethylene levels are relatively low, EIN3 is degraded, and the inhibition of WDL4 expression is released. WDL4 accumulates and promotes hook opening by influencing the auxin maxima and PIN protein distribution and trafficking. The question mark indicates the yet-unknown mechanism by which WDL4 regulates auxin distribution and the trafficking of auxin efflux carriers during hook opening.