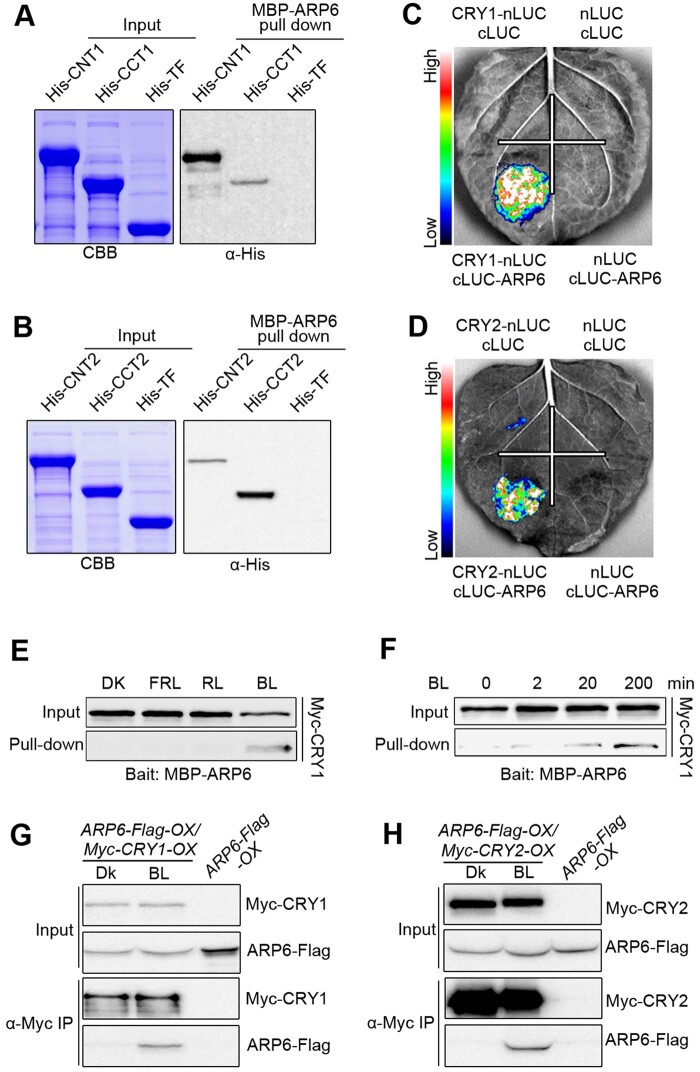
Figure 2.
CRY1 and CRY2 interact with ARP6 in a BL-dependent manner. A and B, In vitro pull-down assays showing the interactions of CNT1 and CCT1 with ARP6 (A), and CNT2 and CCT2 with ARP6 (B). MBP-ARP6 protein served as bait. His-TF, His-TF-CNT1, -CCT1, -CNT2, and -CCT2 served as prey. His-TF was used as negative control. The pulled-down proteins were detected with anti-His antibody. C and D, Split-LUC assays indicating the interactions of CRY1 (C) and CRY2 (D) with ARP6 in N. benthamiana cells. E, Semi-in vivo pull-down assay showing BL-specific interaction of CRY1 with ARP6. Preys were protein extracts from Myc-CRY1-OX seedlings that were DK-adapted for 2 d and then exposed to BL (30 μmol/m2/s) or RL (30 μmol/m2/s) or FRL (5 μmol/m2/s) light or still adapted in DK for 1 h. F, Semi-in vivo pull-down assay showing that CRY1–ARP6 interaction is enhanced in response to increasing exposure times of BL. Preys were protein extracts from Myc-CRY1-OX seedlings that were DK-adapted for 2 d and then exposed to BL (30 μmol/m2/s) for different times. G and H, Co-IP assays showing BL-induced interactions of CRY1 and CRY2 with ARP6 in Arabidopsis. Myc-CRY1-OX Myc-CRY2-OX or ARP6-Flag-OX/Myc-CRY1-OX or ARP6-Flag-OX/Myc-CRY2-OX seedlings were adapted in DK for 2 d and then exposed to BL (30 μmol/m2/s) or still adapted in DK for 1 h, followed by IP with anti-Flag antibody. The IP (ARP6) and co-IP signals (CRY1 and CRY2) were detected by immunoblots probed with anti-Flag and -Myc antibodies.