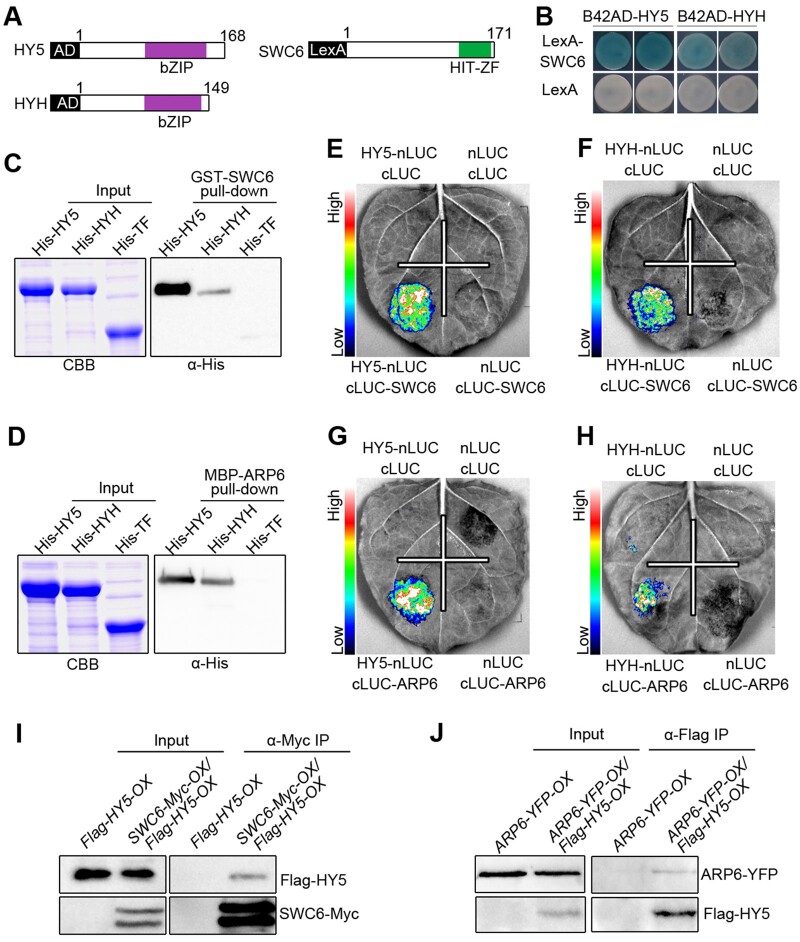
Figure 6.
SWC6 and ARP6 interact with HY5 and HYH. A, Schematic diagram of HY5, HYH, and SWC6 proteins tested in LexA yeast two-hybrid assays. bZIP denotes basic leucine zipper domain. B, LexA yeast two-hybrid assays showing interactions of SWC6 with HY5 and HYH. Yeast cells coexpressing the indicated combinations of constructs were grown on SD –Trp–His–Ura with X-gal. The blue precipitates on the plates represent the GUS activities. C and D, In vitro pull-down assays showing the interactions of HY5 and HYH with SWC6 (C) and ARP6 (D). GST-SWC6 and MBP-ARP6 protein served as baits. His-TF, His-TF-HY5, and -HYH served as preys. Input images show CBB staining. The pulled-down proteins were detected with anti-His antibody. E–H, Split-LUC assays indicating the interactions of SWC6 with HY5 (E) and HYH (F), and the interactions of ARP6 with HY5 (G) and HYH (H). I and J, Co-IP assays showing the interactions of HY5 with SWC6 (I) and ARP6 (J) in Arabidopsis. Flag-HY5-OX and SWC6-Myc-OX/Flag-HY5-OX seedlings were grown in BL (30 μmol/m2/s) for 7 d, followed by IP with anti-Myc antibody. The IP (SWC6) and co-IP signals (HY5) were detected by immunoblots probed with anti-Myc and -Flag antibodies (I). ARP6-YFP-OX and ARP6-YFP-OX/Flag-HY5-OX seedlings were grown in BL (30 μmol/m2/s) for 7 d, followed by IP with anti-Flag antibody. The IP (HY5) and co-IP signals (ARP6) were detected by immunoblots probed with anti-Flag and -YFP antibodies (J).