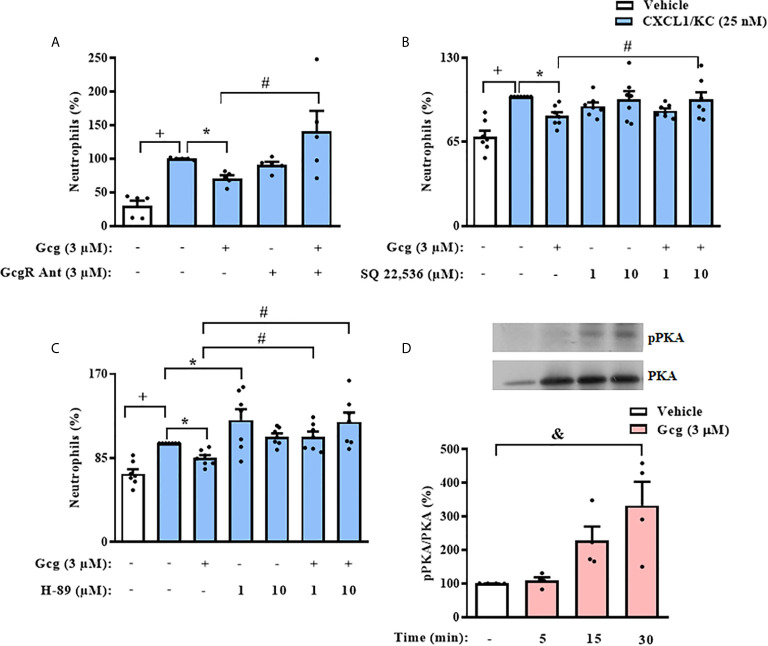
Figure 6.
The inhibition of neutrophil chemotaxis by glucagon in vitro depends on the cAMP-PKA pathway. Cells were pretreated 30 min with GcgR antagonist (A), adenylyl cyclase inhibitor SQ 22,536 (B), or PKA inhibitor H-89 (C) and, after this, treated with glucagon for 30 min in vitro. Then, cells were let to migrate for 40 min towards CXCL1/KC (25 nM) in a chemotaxis chamber. The vehicles used were DMSO 0.1% to SQ 22,536 or medium to glucagon and H-89. (D) Representative samples of pPKA and total PKA expression in the neutrophils of glucagon-treated (3 µM) cells. The expressions of pPKA and total PKA were determined by western blot. Data were normalized to total PKA. Full-length blots of pPKA and total PKA are reported in Supplementary Figure S6 . Each value represents the mean ± S.E.M. BM-neutrophils obtained from 5 (A), 7 (B, C), and 4 (D) random male mice were equally distributed in all experimental groups. The statistical analysis was performed by one-way ANOVA, followed by Newman–Keuls–Student’s t-test. Results from (A–C) are representative of two individual assays. Results from (D) are representative of one individual assay. +++ P < 0.001 compared to non-stimulated cells. * P < 0.05 compared to stimulated cells. # P < 0.05 compared to stimulated cells treated with glucagon. & P < 0.05 compared to non-stimulated cells treated with vehicle. Gcg, Glucagon; GcgR Ant, Glucagon receptor antagonist.