Figure 4. Enzyme-driven biological sensors.
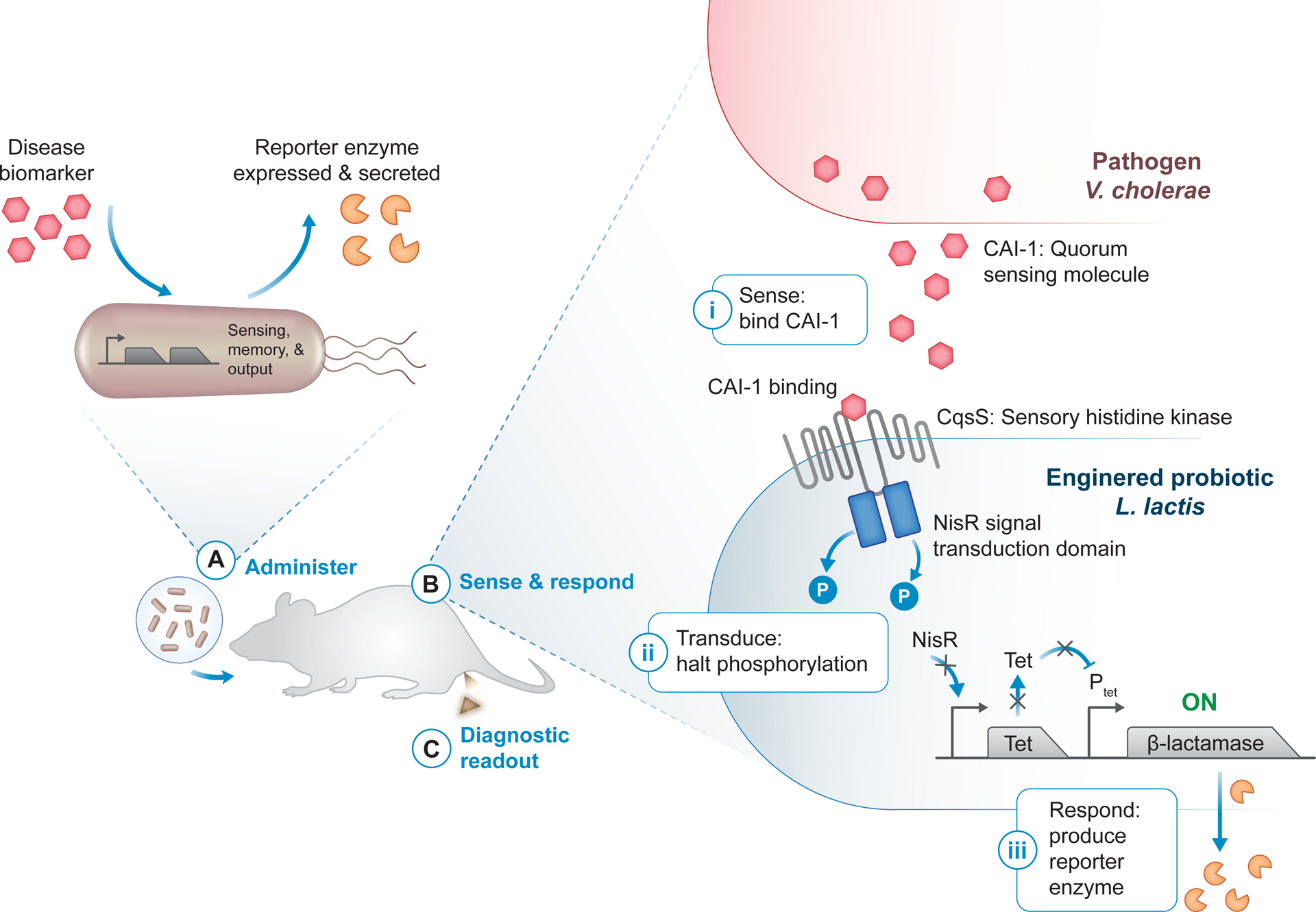
(A) Bacteria modified with sense-and-respond systems use disease-specific biomarkers (red hexagon) to sense a disease state and, in turn, produce a diagnostic readout. Synthetic reporter enzymes such as β-lactamase (orange pacman) can be expressed as a way to generate an activity-based readout of disease state. The engineered probiotic diagnostics can then be administered in vivo, for example orally for diagnostic applications in the gastrointestinal tract. (B) Quorum signaling through cholera autoinducer 1 (CAI-1, red hexagon) in Vibrio cholerae has been used to induce expression of the reporter enzyme β-lactamase in Lactococcus lactis engineered as a cholera diagnostic [100]. The engineered V. cholerae-sensing circuit consists of a hybrid two-component system, comprised of the sensory histidine kinase CqsS linked to the NisR signal transduction domain, and a TetR/Ptet reporter module. Upon CAI-1 binding to CqsS (i), phosphorylation through the two-component system is halted, preventing TetR expression and Ptet repression (ii). Without TetR, the β-lactamase reporter is freely expressed and secreted (iii). (C) An activity assay for the reporter enzyme can be used to produce a diagnostic readout, for example directly in collected fecal samples [100].
