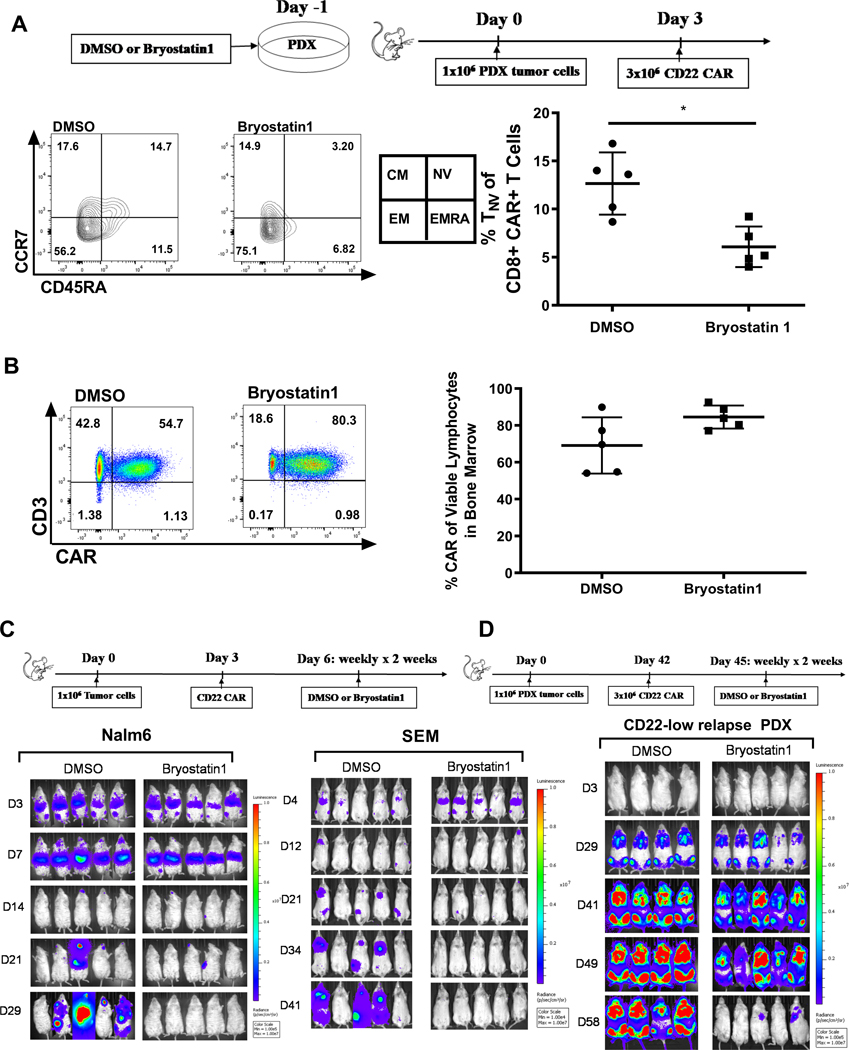
Figure 6: Bryostatin1 treatment pre-CAR infusion alters T cell phenotype without T cell exhaustion, and post-CAR infusion improves durability of remission in vivo.
(A) Nalm6 cells were exposed to 1nM Bryostatin1 for 24 hours, then injected into mice on Day 0. CD22 CAR T cells were administered on Day 3 and mice were sacrificed on Day 10. Bone marrow cells were stained for flow cytometry and analyzed on Fortessa Flow machine. Statistics were calculated using unpaired t-test (* p < 0.0332). (B) NSG mice were injected with Nalm6 on Day 0, CD22 CART on Day 3, and then were given either DMSO control or Bryostatin1 at 40ug/kg once weekly for 2 weeks. Mice were sacrificed 30 days after tumor injection. Cells were stained for flow cytometry and analyzed on Fortessa Flow machine. (C) NSG mice were injected with 1×106 GPF-positive Nalm6 or SEM tumor cells on Day 0. On Day 3, either 3×106 (Nalm6) or 2×106 (SEM) Mock or CD22 CAR were injected for treatment. Mice were given 40ug/kg of Bryostatin1 or DMSO once weekly for 2 weeks. Mice were imaged using IVIS technology and luciferin-D IP injections. (D) NSG mice were injected with 1×106 GPF-positive PDX tumor cells on Day 0. On Day 42, 3×106 Mock or CD22 CAR were injected for treatment. Mice were given 40ug/kg of Bryostatin1 or DMSO once weekly for 2 weeks starting on Day 45. Mice were imaged using IVIS technology and luciferin-D IP injections.