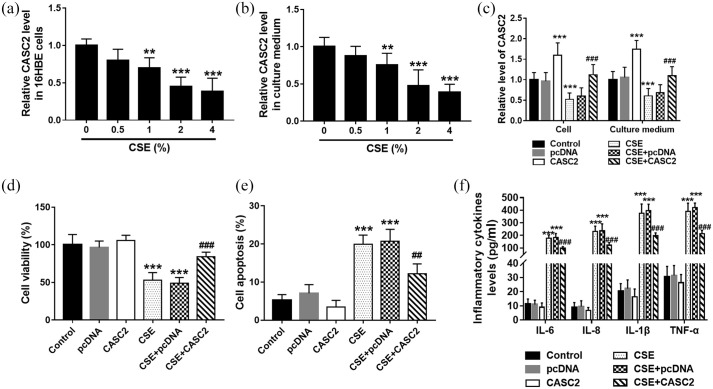
Figure 2.
CASC2 overexpression alleviated CSE-induced apoptosis and inflammation in 16HBE cells. (a) The levels of CASC2 decreased gradually in 16HBE cells as the CSE concentration increased, and the CASC2 levels were significantly suppressed at 2% and 4% CSE concentration. **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001. (b) The levels of CASC2 decreased gradually in the cell culture medium as the CSE concentration increased, and the CASC2 levels were significantly suppressed at 2% and 4% CSE concentration. **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001. (c) CASC2 was significantly upregulated in both cells and cell culture medium by pcDNA-CASC2 transfection. ***p < 0.001, compared with control group; ###p < 0.001 compared with CSE group. (d) and (e) CASC2 overexpression significantly promoted cell viability, while it inhibited CSE-induced cell apoptosis. ***p < 0.001, compared with control group; ###p < 0.001 compared with CSE group. (f) CSE promoted the release of IL-6, IL-8, IL-1β, and TNF-α in 16HBE cells, which was reversed by CASC2 overexpression. ***p < 0.001, compared with the control group; ###p < 0.001 compared with CSE group. Differences between groups were compared using one-way analysis of variance.
CASC2, cancer susceptibility candidate 2; CSE, cigarette smoke extract; pcDNA, plasmid cloning DNA.