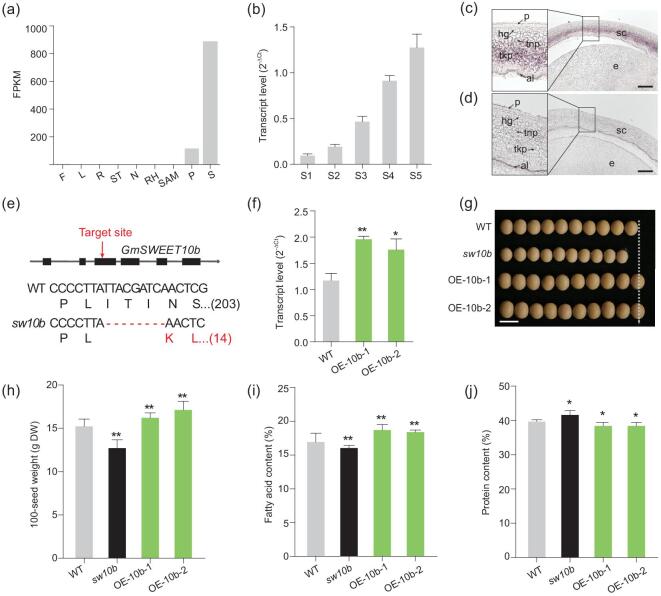
Figure 4.
Effect of GmSWEET10b on seed size, fatty-acid content and protein content. (a) Expression pattern of SWEET10b in different organs in Glycine max (Gm). Expression values were obtained from Phytozome 12 (https://phytozome.jgi.doe.gov/pz/-portal.html#). F, flower; L, leaf; R, root; ST, stem; N, nodule; RH, root hair; SAM, shoot apical meristem; P, pod; S, seed; FPKM, fragments per kilobase of exon per million mapped. (b) Transcript abundance of GmSWEET10b in seed coats at different stages. The expression was detected by reverse transcriptase quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR). Transcript levels were calculated relative to soybean cyclophilin 2 (GmCYP2). (c) and (d) RNA in situ hybridization of GmSWEET10b showing specific expression in the seed coats. Cross-sections of developing seeds at S2–S3 hybridized with antisense (c) or sense probes (d) for GmSWEET10b. sc, seed coat; e, embryo; p, palisade layer; hg, hourglass; tnp, thin-walled parenchyma; tkp, thick-walled parenchyma; al, aleurone layer. Scale bars, 200 μm. (e) Genotypes of the sw10b mutant edited by CRISPR/Cas9 system. The arrow indicates the target site in the region of exon 3 of GmSWEET10b. Changes in DNA sequence in the targeted region and amino-acid sequence of the sw10b mutant are highlighted in red. Numbers inside brackets indicate the number of amino acids coded by the sequence. (f) Increased expression of GmSWEET10b was achieved in transgenic soybean lines OE-10b-1 and OE-10b-2 by introducing additional copies of the genomic sequence into the Williams 82 cultivar. (g) Seed appearance of sw10b mutant and overexpression lines. Scale bars, 1 cm. (h)–(j), 100-seed weight (h), fatty-acid content (i) and protein content (j) of mature seeds from wild-type (WT), sw10b mutant, OE-10b-1 and OE-10b-2. DW, dry weight. Data are means ± s.d. ((h) n = 10; (i) and (j), n = 5). *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01 (Student's t-test).