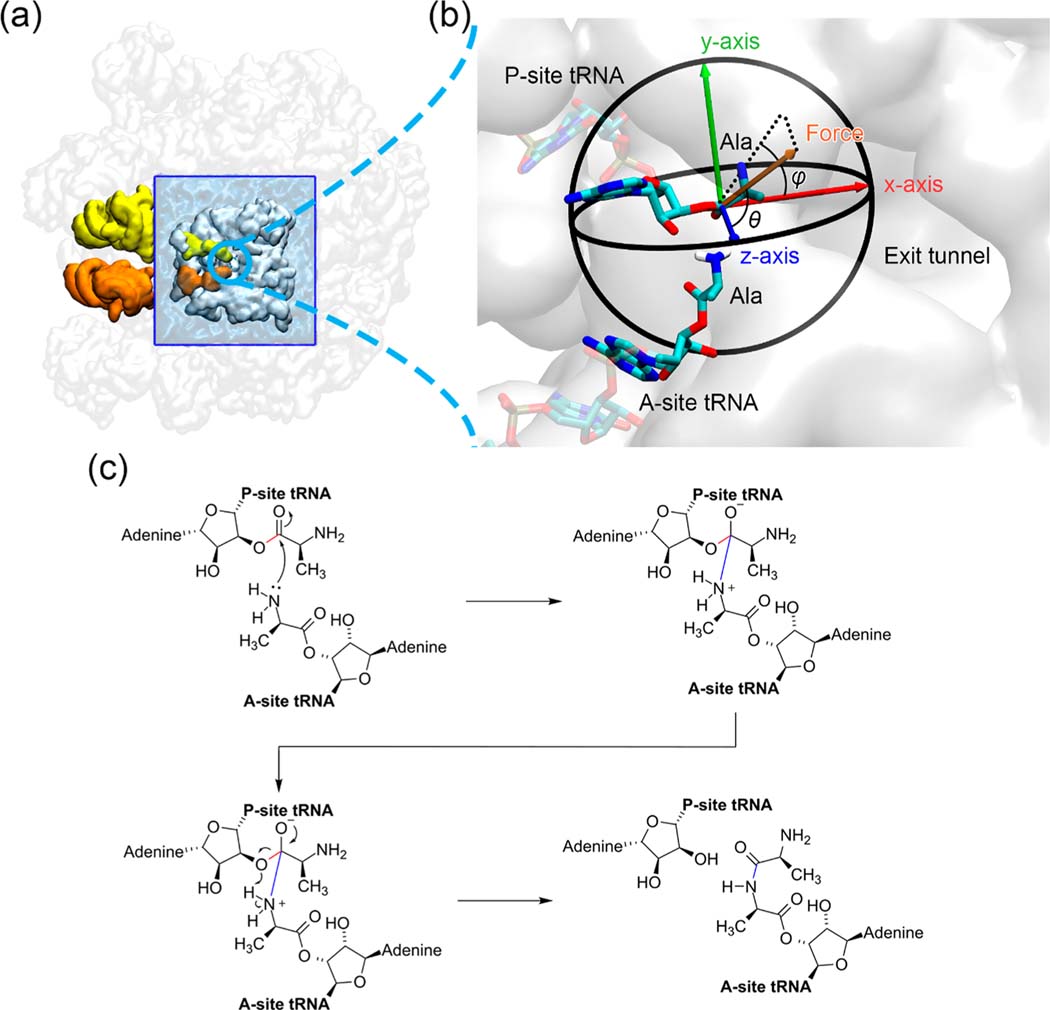
Figure 1.
Simulation system of the peptidyl transfer reaction catalyzed by the E. coli ribosome. (a) Truncated 50S ribosome of the cryo-EM structure 5JTE from the Protein Data Bank. The entire 50S subunit is colored in transparent white. The truncated portion of the ribosome around the peptidyl transferase center (PTC) is shown in opaque white and embedded within a water box (blue). The A- and P-site tRNAs are shown in orange and yellow, respectively. (b) Spherical coordinate system of the pulling force applied on the carbonyl carbon atom of P-site Ala residue. It is a zoomed-in scene of the blue circled region in (a). The most probable structures of the Ala residues from molecular dynamics simulations in the reactant state are shown here, and the atoms treated quantum mechanically are represented as opaque sticks. (c) Reaction scheme of the peptidyl transfer reaction catalyzed by the ribosome and modeled in our QM/MM simulations. The breaking 3′ O–C bond in the P-site tRNA A76 nucleotide residue and the forming A- and P-site peptide bond, which are used to define the reaction coordinate, are highlighted in red and blue, respectively.