Fig. 1. Bile acid and oxysterol synthesis in the liver and other tissues.
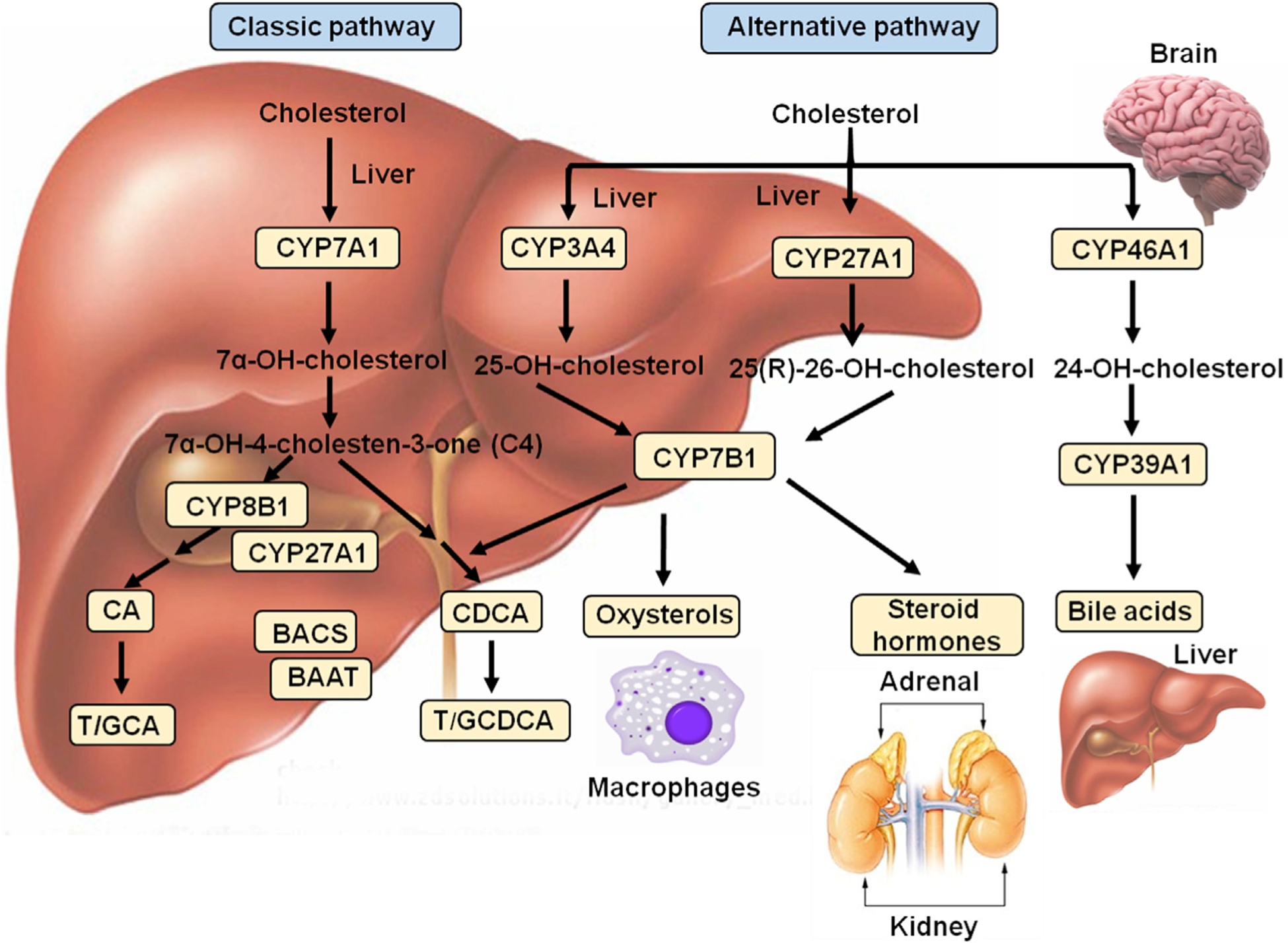
The liver is the only organ that expresses all the enzymes required for bile acid synthesis in the classic bile acid synthesis pathway. The alternative pathways exist in macrophages, adrenal and brain. The classic pathway of bile acid synthesis from cholesterol is catalyzed by cholesterol 7 alpha-hydroxylase (CYP7A1). 7α-hydroxycholesterol is then converted to 7α-hydroxy-4-cholesten-3-one (C4), which is the common precursor for cholic acid (CA) and chenodeoxycholic acid (CDCA) synthesis. C4 is 12α-hydroxylated by sterol 12α-hydroxylase (CYP8B1), producing CA. Without CYP8B1, C4 is converted to CDCA. Mitochondrial sterol 27-hydroxylase (CYP27A1) catalyzes steroid side-chain oxidation to form 3α, 7α, 12α-trihydroxycholestanic acid (THCA) and 3α, 7α-dihydroxycholestanic acid (DHCA). THCA and DHCA are activated by bile acid-CoA synthase (BACS, also known as long-chain acyl-CoA synthase, SLC27A5) for peroxisomal β-oxidation reactions to cleave a propionyl-CoA to form cholyl-CoA and chenodeoxycholyl-CoA, which are conjugated to the amino acids glycine (G) or taurine (T) by bile acid-CoA: amino acid N-acyltransferase (BAAT) to form T/GCA and T/GCDCA, respectively. The alternative bile acid synthesis pathway is initiated by CYP27A1, which converts cholesterol to 25(R)-26-hydroxycholesterol (27-hydroxycholesterol) in the liver. Oxysterol 7α-hydroxylase (CYP7B1) catalyzes 7α-hydroxylation of 27-hydroxycholesterol. In the liver, CYP3A4 catalyzes 25-hydroxylation of cholesterol to 25-hydroxycholesterol, followed by hydroxylation by CYP7B1. CYP27A1 and CYP7B1 are also expressed in macrophages for oxysterol metabolism and in adrenal glands for steroid hormone synthesis. In the brain, cholesterol 24-hydroxylase (CYP46A1) hydroxylates cholesterol to 24-hydroxycholesterol, an abundant sterol in the brain, which can be transported to hepatocytes and 7α-hydroxylated by 24-hydroxysterol 7α-hydroxylase (CYP39A1) for bile acid synthesis.
