Fig. 4. Mechanism of regulation of the CYP7A1 gene.
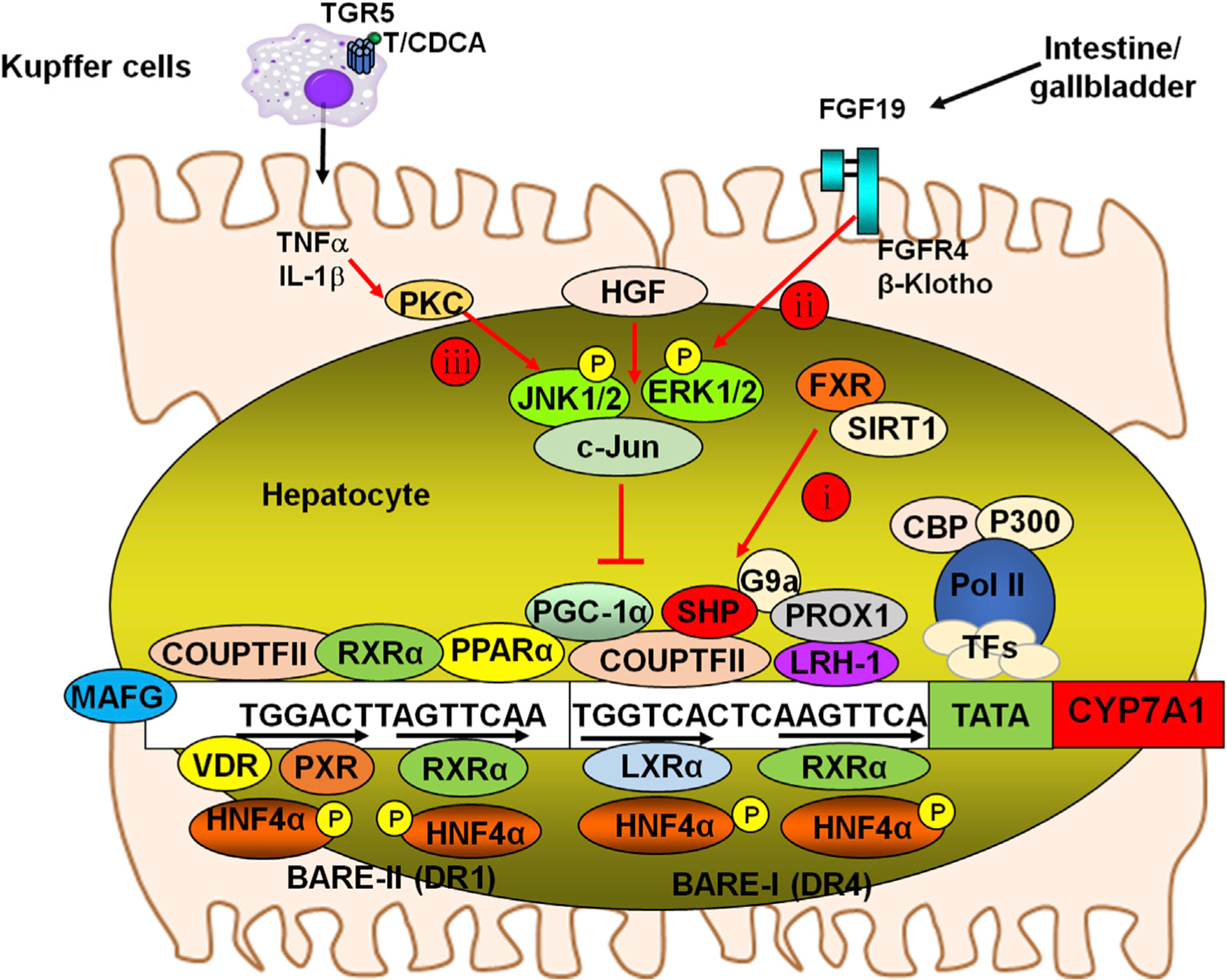
The CYP7A1 gene proximal promoter contains BARE, which binds the nuclear receptors shown. Three mechanisms for bile acid regulation of CYP7A1 gene transcription are illustrated here. The CYP7A1 promoter contains two bile acid responsive elements, BARE-I and BARE-II, which contains a direct repeat with 4 bases spacing (DR4) and 1 base spacing (DR1) motif, respectively. Nucleotide sequences shown are rat Cyp7a1 gene. Mechanisms 1 and 2 are FXR-dependent and mechanism 3 depicts an FXR-independent cell signaling pathway. Mechanism i: Bile acid activation of FXR induces the repressor SHP to inhibit HNF4α and LRH-1-mediated transcriptional activation of CYP7A1. The SHP-mediated mechanisms may also inhibit PXR/RXRα (BARE-II), COUP-TFII/RXRα (BARE-I and BARE-II), LXR/RXRα (BARE-I) and PPARa/RXRα (BARE-II) binding to the CYP7A1 promoter to suppress CYP7A1 gene transcription. FXR also induces MAFG to inhibit CYP7A1. PXR, VDR and PPARa inhibit CYP7A1 gene transcription via competition for HNF4α binding to the BARE-II on the CYP7A1 gene promoter. Mechanism ii: Bile acid activation of intestinal FXR induces FGF19, which is transported from the intestine to the liver and activates the FGFR4/β-Klotho complex to phosphorylate and activate JNK1/2 and ERK1/2 signaling pathways. Phosphorylation of HNF4α inhibits its dimerization and binding to the CYP7A1 gene, resulting in reduced CYP7A1 gene transcription. Phosphorylation of PGC-1α, a co-activator of PPARα, and other nuclear receptors also inhibit trans-activation of the CYP7A1 gene. Mechanism iii: Taurodeoxycholic acid (TDCA)/CDCA activates macrophages and induces the release of inflammatory cytokines including TNFα and IL-1β, which cross the sinusoidal membrane to activate protein kinase C (PKC) and JNK signaling pathways to inhibit CYP7A1 gene transcription. Epigenetic regulation: Histone acetylases (HATs), such as CBP/P300 and histone deacetylases (HDACs) such as sirtuin 1 (SIRT1), regulate FXR, SHP and CYP7A1/CYP8B1 by epigenetic mechanisms. The methytransferase G9a is recruited by SHP and Prox-1 to inhibit CYP7A1 by histone methylation. Abbreviations: CYP7A1, cholesterol 7 alpha-hydroxylase; BARE, bile acid response elements; HNF4α, hepatocyte nuclear factor 4 alpha; FXR, farnesoid X receptor; FGFR4, fibroblast growth factor receptor 4; CDCA, chenodeoxycholic acid; JNK, c-Jun N-terminal kinase; SHP, small heterodimer partner; LRH-1, liver-related homologue-1; PXR, pregnane X receptor; VDR, vitamin D receptor; PPAR, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor.
