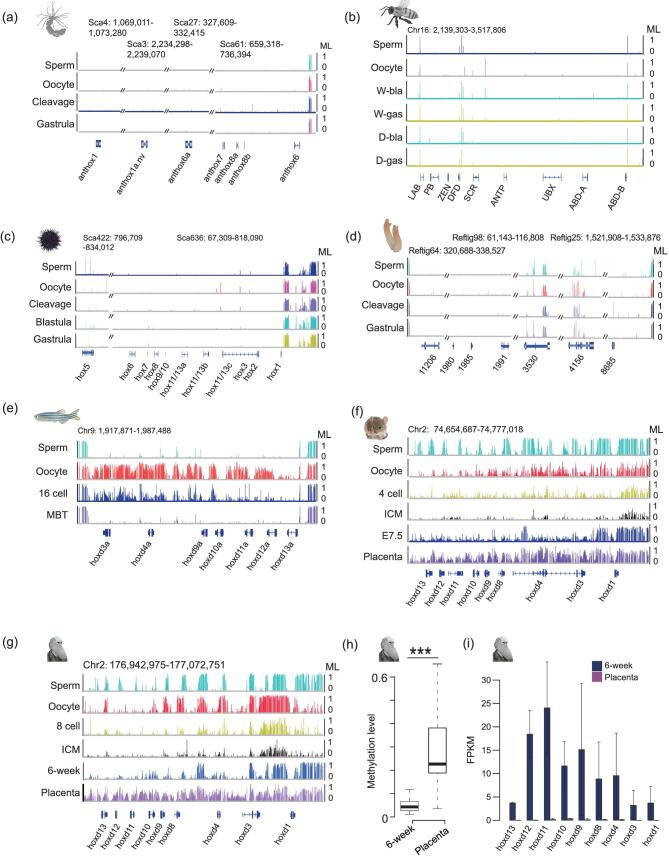
Figure 4.
Methylation of the HOX gene clusters in different taxa. (a)–(d) Genomic snapshots representing methylation of the HOX gene clusters in sperm, oocytes and early embryos of sea anemone (a), honey bee workers and drones (b), sea urchin (c) and sea squirt (d). Oblique lines represent regions of the HOX cluster that are non-contiguous or interrupted. (e)–(g) Genomic snapshots show methylation dynamics of HOX gene clusters in zebrafish (e), mouse (f) and human (g). (h) Boxplots show the promoter methylation levels (MLs) of HOX genes between 6-week embryos and placenta in human. P value was calculated by paired Wilcoxon signed-rank test. ***P < 0.001. (i) Normalized expression levels of HOXD genes in human 6-week embryos and placenta. FPKM stands for fragments per kilobase of transcript per million mapped reads.