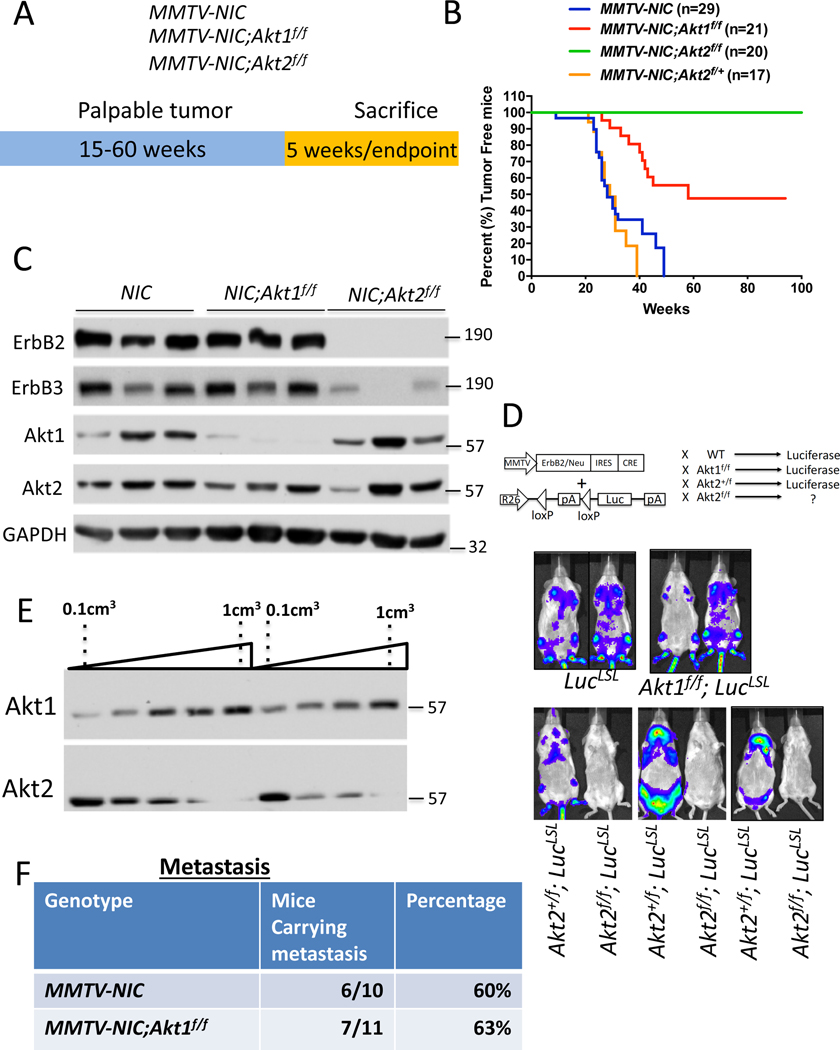
Figure 1: The effect of the Akt1 or Akt2 cell autonomous deletion on ErbB2-mediated mammary primary tumors and metastasis.
A. The genotypes of mice and experimental strategy. Mice were euthanized at 5 weeks after tumor palpation, for immunoblotting, and at endpoint when tumors reached 2cm in diameter. B. Kaplan-Meier plots showing percent of tumor free mice as determined by the time tumor is palpated, of MMTV-NIC, MMTV-NIC-Akt1f/f, MMTV-NIC-Akt2f/f and MMTV-NIC-Akt2+/f mice. The number of mice is indicated. p<0.0001 MMTV-NIC versus MMTV-NIC-Akt1f/f and MMTV-NIC-Akt2f/f, p>0.05, MMTV-NIC versus MMTV-NIC-Akt1+/f using the log-rank test. C. Immunoblot showing ErbB2, ErbB3, Akt1 and Akt2 protein expression in the mammary glands of MMTV-NIC, MMTV-NIC;Akt1f/f and MMTV-NIC;Akt2f/f mice. Akt2 is not co-expressed with ErbB2 (see text). D. Luminescent imaging showing luciferase expression in MMTV-NIC;LSL-Luc, MMTV-NIC;Akt1f/f;LSL-Luc, MMTV-NIC;Akt2+/f;LSL-Luc, and MMTV-NIC;Akt2f/f;LSL-Luc mice. E. Representative immunoblot showing the expression of Akt1 and Akt2 during primary tumor development in MMTV-NIC mice. F. Table summarizing the incidence of lung metastasis in MMTV-NIC and MMTV-NIC;Akt1f/f mice. The mice were sacrificed at the primary tumor endpoint, and the lungs were scored for metastasis.