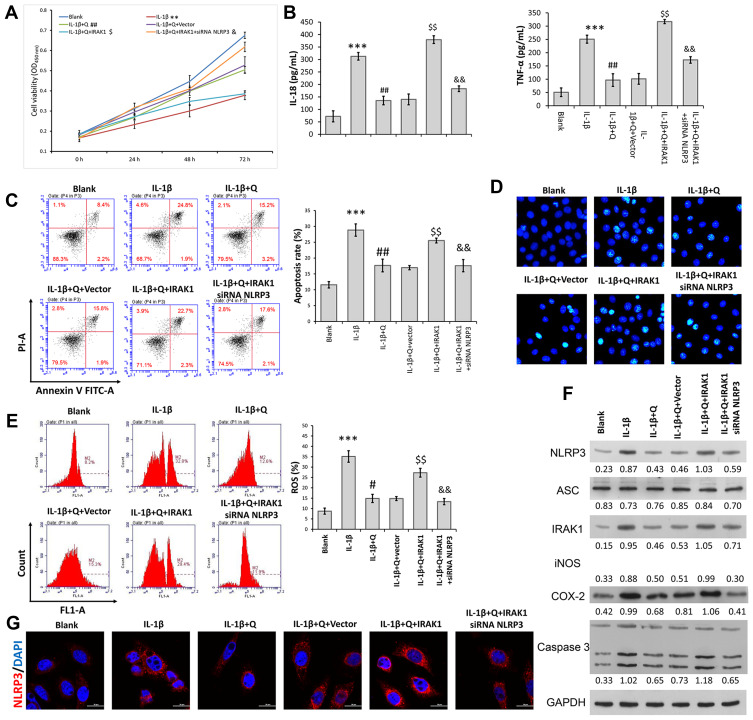
Figure 4.
Quercetin inhibited IL-1β-induced rat chondrocyte injuries in vitro by suppressing the IRAK1/NLRP3 signaling pathway. Chondrocytes in the IL-1β + quercetin group were transiently co-transfected with siRNA targeting NLRP3 (si-NLRP3) and an IRAK1 overexpression plasmid. (A) Chondrocyte viability was analyzed by the CCK-8 assay. (B) The levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-18 and TNF-α) were determined by ELISA. (C) Cell apoptosis was evaluated by flow cytometry performed with an Annexin V-FITC/propidium iodide (PI) apoptosis kit. (D) Hoechst 33342 staining was performed. Apoptotic cells exhibited morphological changes in the nuclei typical of apoptosis. Images were captured under a fluorescence microscope. (E) The intracellular levels of ROS in chondrocytes were assessed using a DCFH-DA probe. (F) The levels of NLRP3, ASC, iNOS, COX-2 and IRAK1 proteins were assessed by Western blotting. (G) NLRP3 immunofluorescence staining. Markedly increased red bright puncta indicated the upregulated expression of NLRP3 (bar: 20 μm). Data represent a mean value ± standard deviation. **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, compared with blank; #p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01, compared with IL-1β; $p<0.05, $$p < 0.01, compared with IL-1β + quercetin + vector; &p < 0.05, &&p < 0.01, compared with IL-1β + quercetin + IRAK1.