Figure 5.
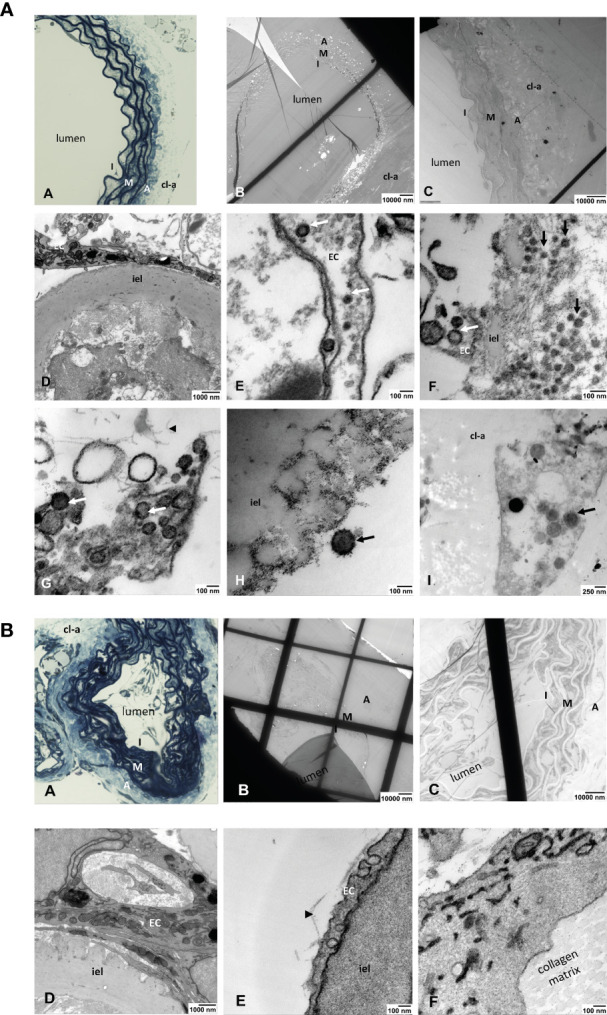
(A) Light and electron microscopic analyses of SARS-Cov-2-infected ARA. (A) toluidine blue-stained aortic wall section displaying the layers intima (I), media (M) and avdentitia (A). (B) Tissue section of SARS-CoV-2-infected ARA in EM with low and (C) higher magnification displaying the aortic wall layers as in (A). (D) Higher magnification shows the aortic intima with EC and inner elastic lamina (iel) (E–I) SARS-CoV-2 viral particles (arrows) in a EC process into the aortic lumen (E), in the intimal layer (arrows) (F), inside of an EC process within the collagen matrix (arrowhead) (G), attached to the inner elastic lamina (iel) (H), in a cell that was migrated into the collagen gel (cl-a) around the aortic wall (I). I: intima, M: media, A: adventitia; EC: endothelial cell; cl-a: collagen gel around the aortic wall; iel: inner elastic lamina of the aortic wall. (B) Light and electron microscopic analyses of non-infected ARA. (A) Toluidine blue-stained aortic wall section displaying the layers intima (I), media (M) and adventitia (A). (B, C) tissue section of non-infected ARA in EM with low and higher magnification displaying the aortic wall layers as in A. (D–F): No SARS-CoV-2 viral particles were detected in the cells of the aortic wall, neither in ECs of the intima (D, E) nor in those sprouted into the collagen matrix (F). I: intima, M: media, A: adventitia; cl-a: collagen gel around the aortic wall; iel: inner elastic lamina of the aortic wall.
