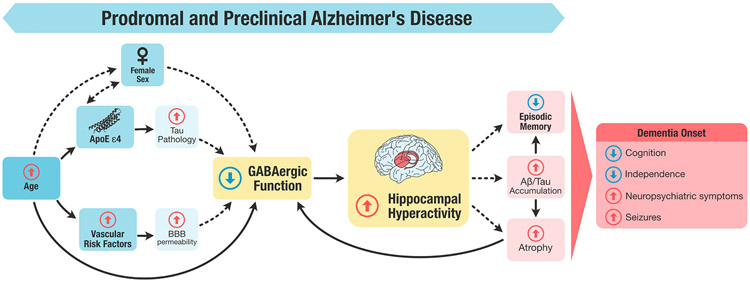
Fig. 1.
Figure representing the role of the GABAergic system in memory impairment during the prodromal or preclinical stages of AD. GABAergic dysfunction results from a combination of factors working independently, and in interaction, including an increase in age, female sex, the presence of APOE ε4 polymorphism, and vascular risk factors. The reduction of GABA levels precipitates hippocampal hyperactivity, which in turn contributes to episodic memory impairments that are concomitant with or precede the incidence of dementia. Dashed lines represent those relationships that need further research to be confirmed. Note: Aβ, amyloid β; APOE ε4, apolipoprotein ε4 polymorphism; BBB, Blood brain barrier.